7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
The Buddhas of Bamiyan

NIMAS expedition team to Mt Everest
Peace dividend
The Citizenship (Amendment) Bill, 2016
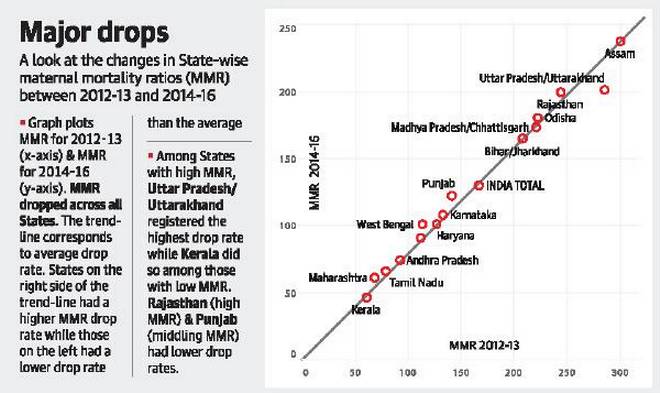
Maternal mortality ratio
IND-INDO CORPAT
Source: PIB, The Hindu