7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
National Tiger Conservation Authority’s (NTCA) proposal to convert Dibang Wildlife Sanctuary into Tiger Reserve has attracted protests from Idu Mishmis.
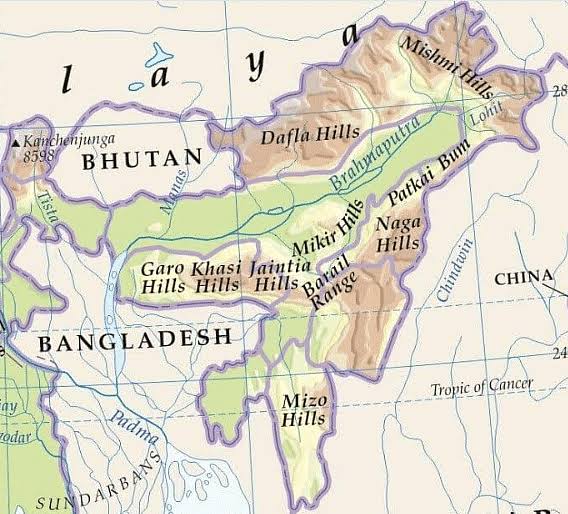
Tribes of Arunachal Pradesh - Adi, Nishi, Apatani, Tagin, Mishmi, Khampti Nocte, Wancho, Tangshangng, Singpho, Monpa, Sherdu-Kpen and Aka
Community Conserved Area (CCA)
Quick facts
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
References