7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
The Reserve Bank of India has recently launched the e-Rupee for retail users.
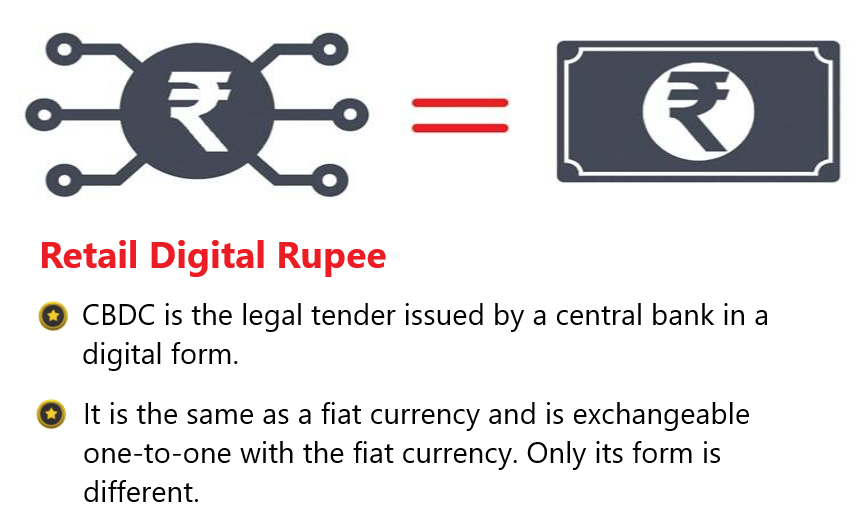
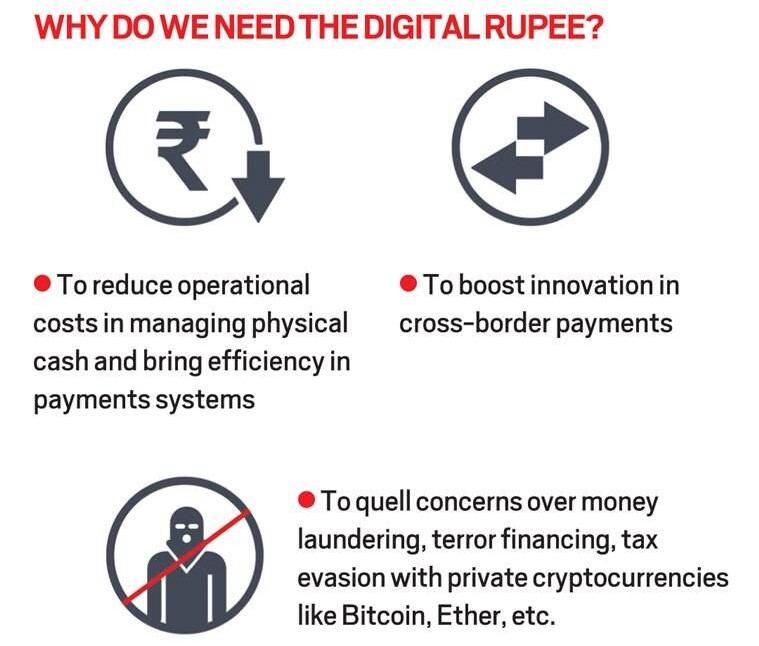
CBDC has the potential to provide significant benefits such as:
Other benefits
Reference