7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
A study by Christian Medical College (CMC) Vellore & London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) highlights the high risk of scrub typhus infections in rural Tamil Nadu.
Key Findings of the Study
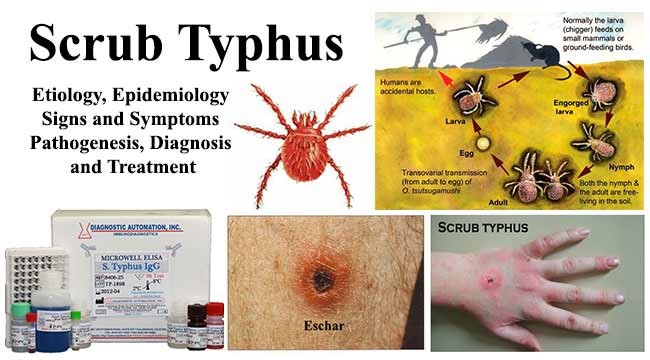
Scrub Typhus