7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
What is the issue?
There is a debate as to whether a large fiscal stimulus would lead to high inflation amidst the deficit financing
What is deficit financing?
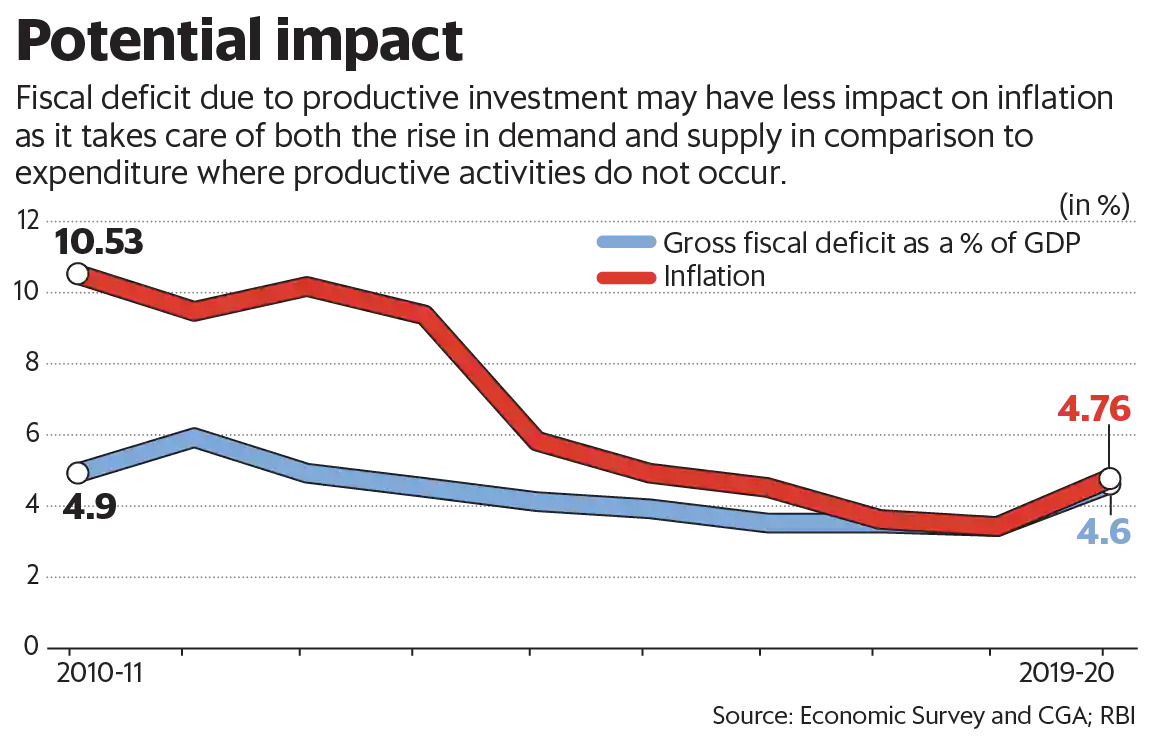
What is the current fiscal scenario?
Fiscal deficit is the difference between total revenue and total expenditure of the government.
It is an indication of the total borrowings needed by the government (so as to finance the deficit).
What does The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act targets for?
What are the feared consequences of rising fiscal deficits?
What is the cause for the current rise in fiscal deficit?
Should the government stop spending?
What measures need to be taken?
Source :The Hindu Businessline