7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
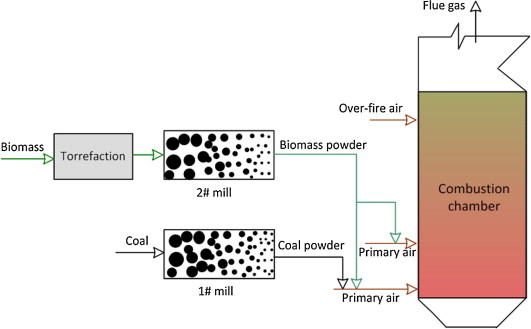
Recently, Ministry of Power revised the policy on biomass thus obligating the thermal power plants to increase the use of biomass pellets.
Biomass Co-firing Policy
References