7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
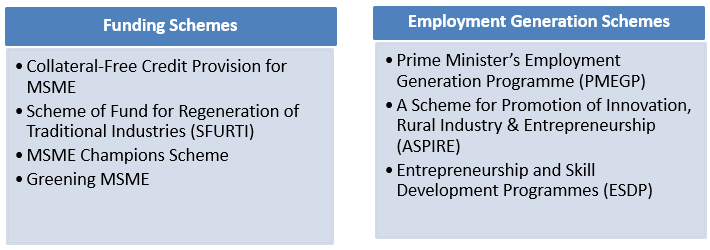
Small Industry Day is observed in India every year on August 30 that recognises the contributions of small businesses and industries to the economy.
|
Classification of Industries |
|||
|
Classification |
Micro |
Small |
Medium |
|
Investment |
Not more than Rs.1 crore |
Not more than Rs.10 crore |
Not more than Rs.50 crore |
|
Annual Turnover |
Not more than Rs. 5 crore |
Not more than Rs. 50 crore |
Not more than Rs. 250 crore |
The United Nations General Assembly officially designated June 27 as MSME Day to increase public awareness of the vital role that MSMEs play in promoting sustainable development and contributing to the global economy.
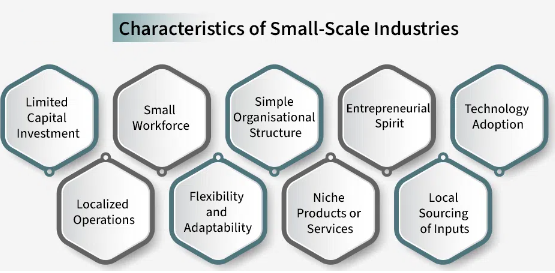
Mahatma Gandhi said that “The salvation of India lies in cottage and small scale industries”.