7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
The Smart Cities Mission (SCM) has experienced a shift in focus within the political landscape, particularly in the context of recent elections and government priorities.
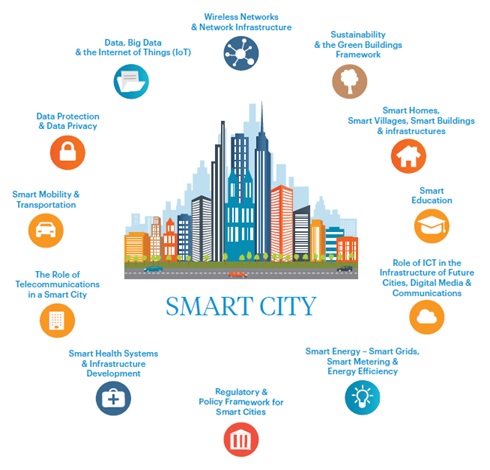
100 cities have been selected to be developed as Smart Cities by 2024 through a two-stage competition.
|
Features |
About |
|
Objective |
|
|
Area based development |
|
|
Key focus areas |
|
|
Fundamental principles of smart cities |
|
References