Recently, a study on Southern ocean “Closing the loops on Southern Ocean dynamics: From the circumpolar current to ice shelves and from bottom mixing to surface waves “ revealed more details on the dynamic nature of Southern Ocean.
Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is the longest, strongest, deepest-reaching current on earth and circulates clockwise around the continent, carrying more water around the globe than any other current.
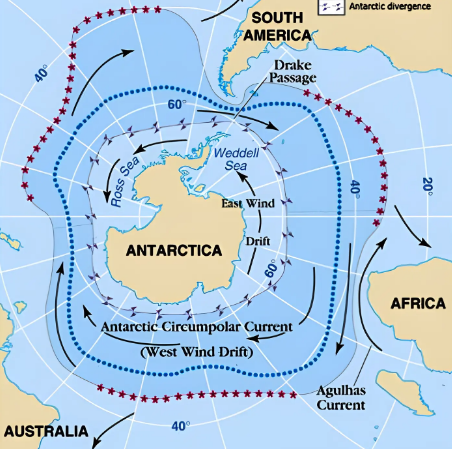
Sothern Ocean acts as a time capsule as it takes hundred year for the ocean water from the surface to sink and return to surface. Water returning to the surface today reflects the cooler, pre-industrial climate when it first sank to the ocean depths.
|
Forms of Ice |
|
2021-2030 is adopted as UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development.
SWOT satellite is a joint project of the European Union and United States to measure the ocean surface at unprecedented resolution