7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
In a recent event, Union Minister of Commerce and Industry accuses e-commerce players of predatory pricing.
|
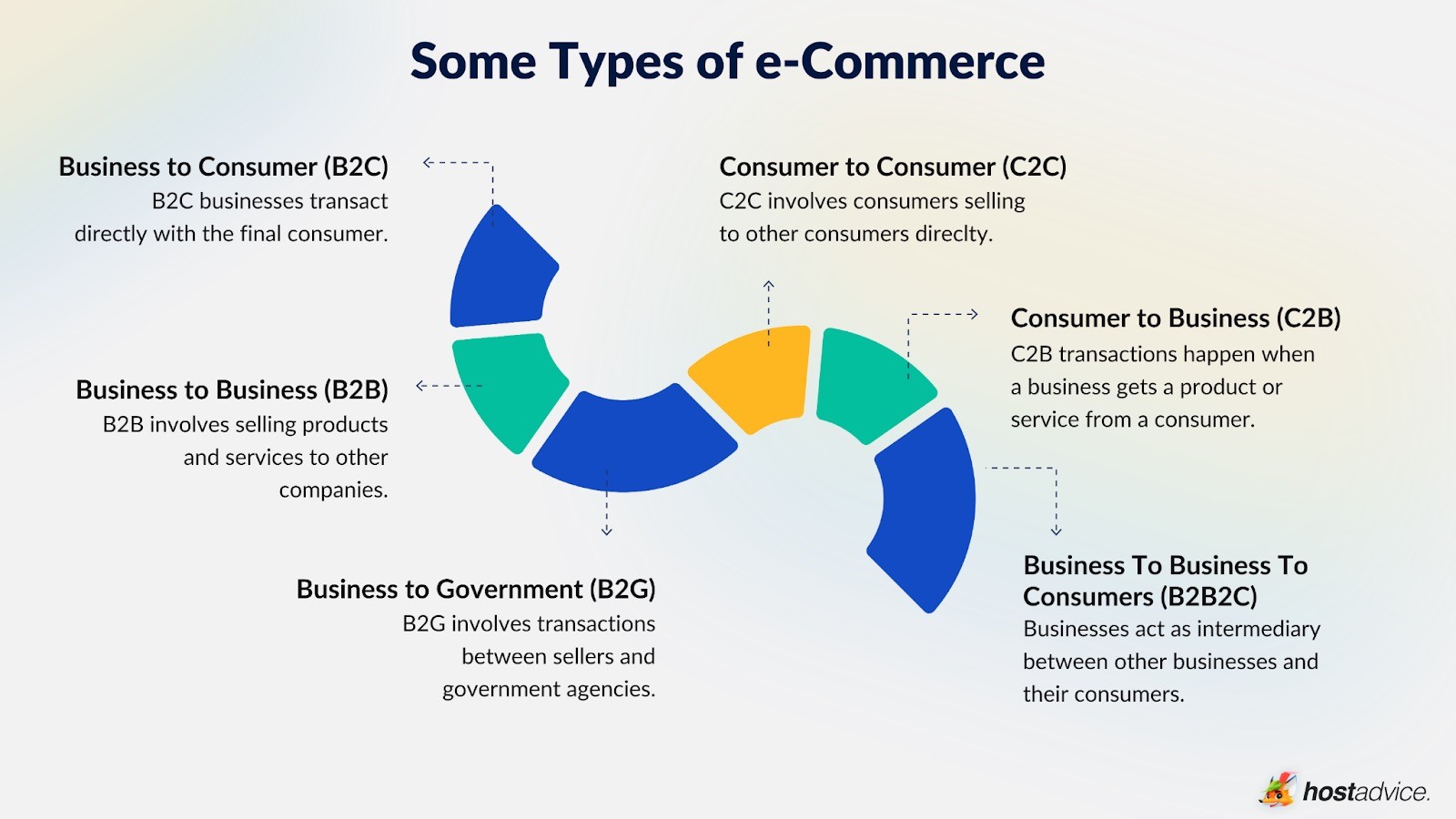
Status of E-Commerce |
|
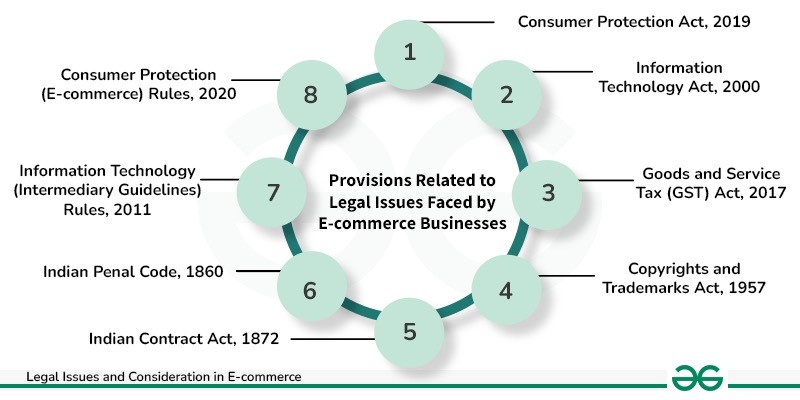
Draft National E-commerce Policy (2019) proposes data localization, regulation of cross-border data flows, addressing anti-competitive practices, and promoting Make in India products. It emphasizes the protection of consumer data and fostering domestic innovation.
Predatory pricing involves selling goods or services at very low prices, often below cost, to eliminate competition and establish a monopoly.
|
Positive Impacts |
|
|
Negative impacts |
|