PART A
SCOPE FOR INDIA
AMRIT KAAL
PRIORITY 1: INCLUSIVE DEVELOPMENT
A. AGRICULTURE AND COOPERATION
India is the largest producer and 2nd largest exporter of Shree Anna in the world
B. HEALTH, EDUCATION AND SKILLING
PRIORITY 2: REACHING THE LAST MILE
PRIORITY 3: INFRASTRUCTURE & INVESTMENT
Operating ratio is the amount of money the railways has to spend to earn Rs 100. A lower operating ratio implies better financial health
PRIORITY 4: UNLEASHING THE POTENTIAL
PRIORITY 5: GREEN GROWTH
PRIORITY 6: YOUTH POWER
PRIORITY 7: FINANCIAL SECTOR
PART B
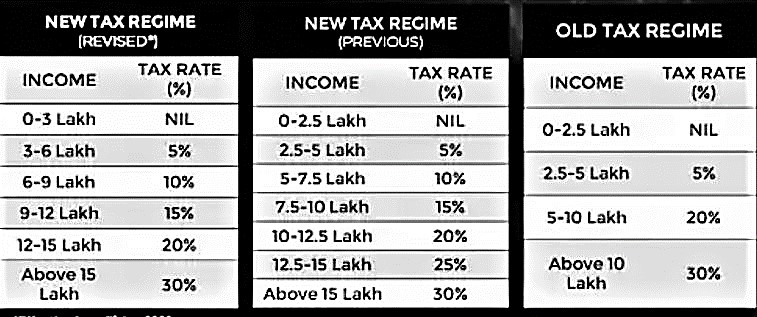
PERSONAL INCOME TAX
INDIRECT TAX
OTHERS
|
Presumptive Taxation Scheme (PTS) |
|
Under the presumptive taxation scheme (PTS), a taxpayer is exempt from maintaining books of accounts as small taxpayers had to bear additional costs in maintain them. It is defined under three different sections—44AD, 44ADA and 44AE—of the Income-tax Act. |