7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
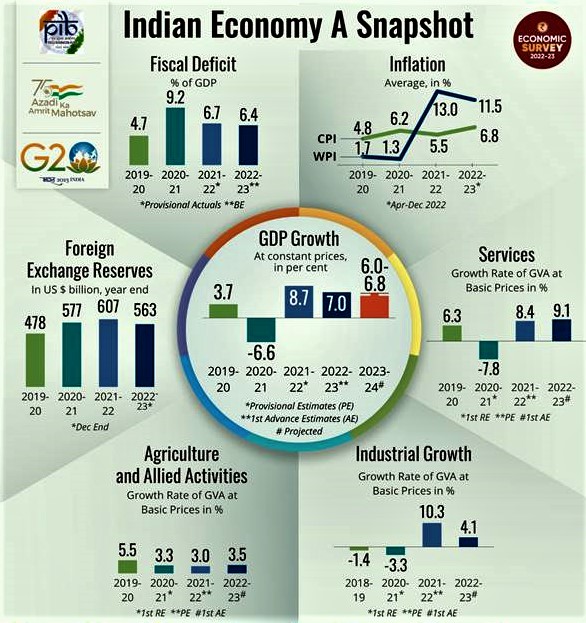
The Economic Survey 2022-23 prepared by a team of economists led by chief economic adviser Anantha Nageswaran analyses developments in the economy in the past year and makes projections for the following year.
References