The Supreme Court has ruled against the telecast ban imposed by the Union Government on Malayalam news channel MediaOne.
|
Sector |
Powers of I&B Ministry |
|
TV channels |
The Ministry has the Electronic Media Monitoring Cell, which tracks channels for any violations of the programming and advertising codes mentioned in the Cable TV Network Rules, 1994. |
|
OTT platforms |
For content on OTT platforms too, there is a similar structure like that of TV channels. |
|
Film certification |
The Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC) has a mandate to give a film, a rating, indicating the kind of audience it is suitable for. While it isn’t the CBFC’s mandate to censor a film, it can withhold giving a rating unless the filmmaker agrees to its suggestions. |
|
Print media |
Based on the recommendations of the Press Council of India, the government can suspend its advertising to a publication. |
|
Websites |
IT rules 2021 allowed the I&B Ministry to issue orders to ban websites based on their content. |
Quick facts
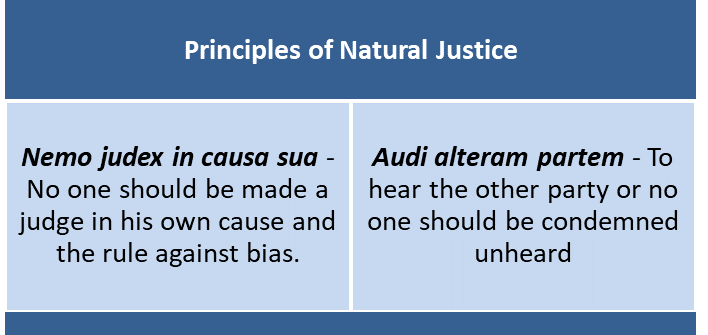
Principle of Natural Justice
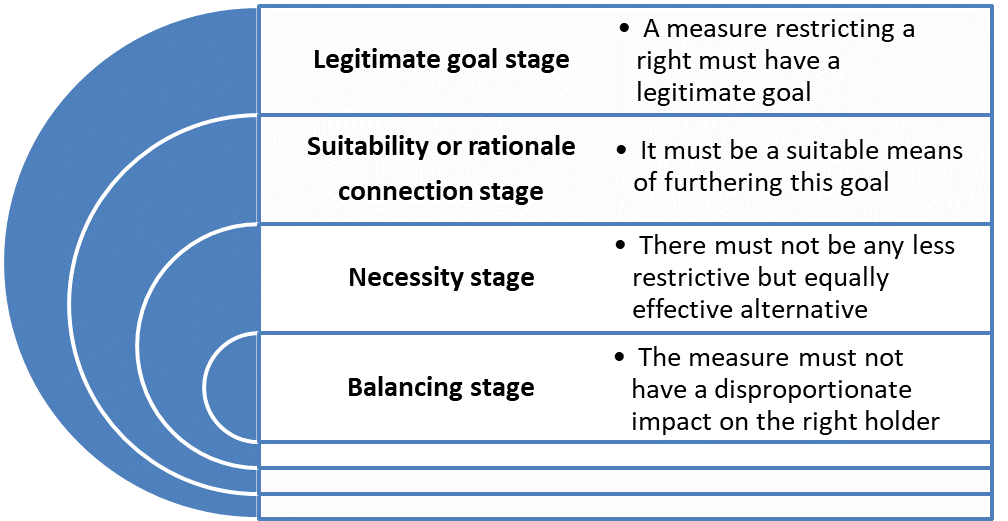
Test of Proportionality
Sealed cover jurisprudence
References