A major earthquake struck Turkey and Syria killing more than 2600 people and flattening thousands of buildings.
Fault - A fracture in the rocks that make up the Earth’s crust
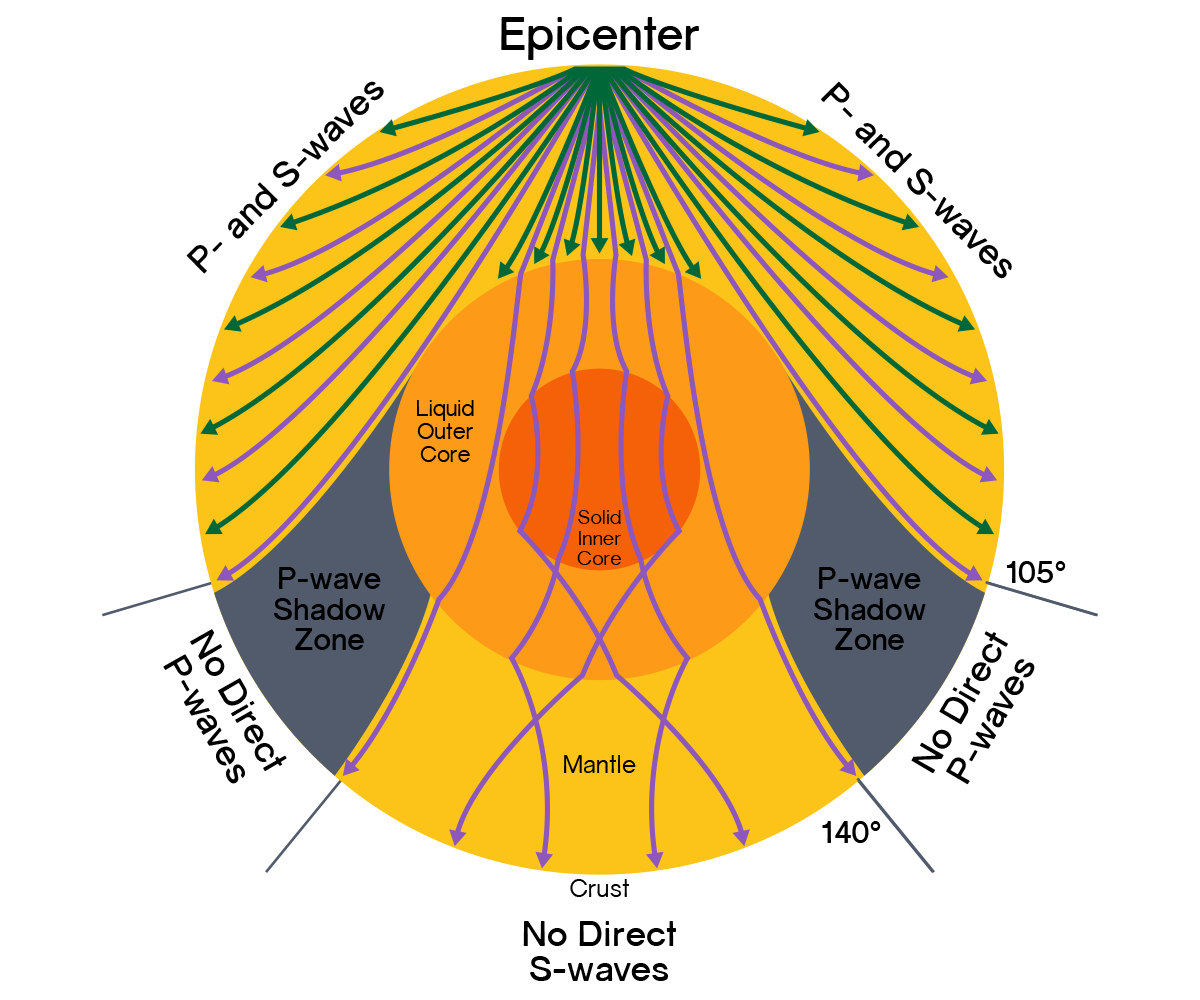
Epicenter - The point at the surface of the Earth above the focus
Plates - Massive rocks that make up the outer layer of the Earth’s surface and whose movement along faults triggers earthquakes
Seismic waves - Waves that transmit the energy released by an earthquake
Focus (Hypocenter) - The point within the Earth where an earthquake rupture starts
Earthquakes

Types of energy waves
Types of earthquake
Earthquake prone zones
Measuring the magnitude
Measuring the intensity
|
S.No |
Richter Scale |
Mercalli Scale |
|
1. |
Has 10 levels |
Has 12 levels |
|
2. |
Measures the magnitude of earthquake |
Measures the intensity of earthquake |
|
3. |
Only describes the strength at the focal point |
Describes damages at multiple locations |
What are aftershocks and why do they occur?
According to an estimate, almost 95% of the country’s land mass is prone to earthquakes, while about a third of the country is at high risk.
The Erzincan earthquake measured 7.8 on the Richter scale, occurred on the North Anatolian Fault Zone (NAFZ), and created a 360-km-long surface rupture.
It killed about 33,000 people and caused extreme damage in the Erzincan Plain and the Kelkit River Valley.
References