Recently, the Rajya Sabha passed the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024.
References
Recently, the Indian rock python species have declined across Tamilnadu, but they are being spotted with increasing frequency in Mudumalai Tiger Reserve and Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve.

There are no records of Indian Rock Python attacking people in India according to the Wildlife Institute of India.
References
PM-WANI framework is making significant strides in enhancing internet accessibility across India, with over 18.19 lakh unique users and 58.55 petabytes (PB) of data consumed.
Reference
PIB | Prime Minister's Wi-Fi Access Network Interface (PM-WANI)
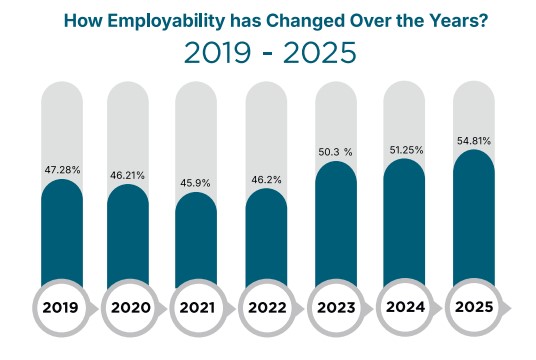
India Skills Report 2025 (ISR 2025)
Recently, the India Skills Report 2025 stated that Kerala ranked 5th among the top States, maintaining a strong employability rate of 71%.
Report Findings
References
Diamond Battery
Scientists and engineers from UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) have created a Diamond Battery with the potential to power devices for thousands of years.
Reference