The 7th Session of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) was held in New Delhi from November 3 to 6, 2024.
The founding conference of ISA was held on March 11, 2018, in India marked a significant step in mobilizing international efforts toward solar deployment.
Achieving these targets would significantly mitigate global carbon emissions, reducing 1,000 million tonnes of CO2 annually.
Initially focused on developing countries, the ISA's Framework Agreement was amended in 2020 to allow all United Nations member states to join.
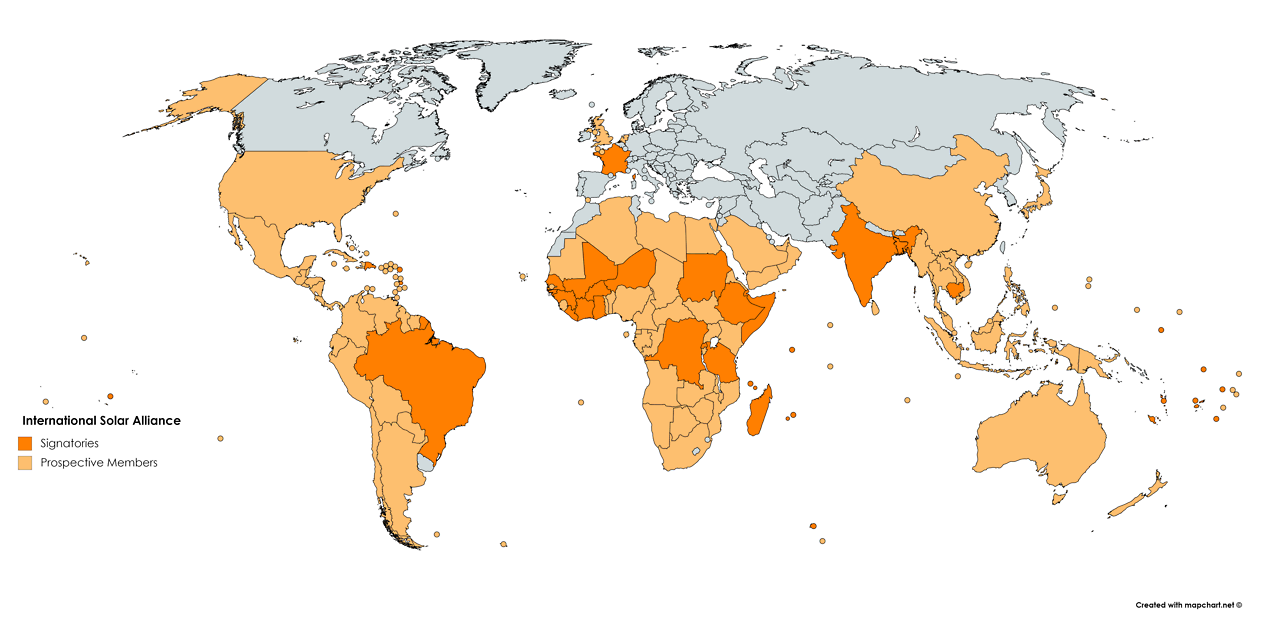
The seventh session of the ISA Assembly elected Mr. Ashish Khanna from India as its third Director General.
|
ISA Initiatives |
|
|
SolarX Startup Challenge |
It was introduced at COP27(2022) to support innovative solar businesses in ISA Member Countries. |
|
STAR-C Initiative |
To strengthen solar technology skills in developing economies. |
|
Global Solar Facility |
To catalyse investment in underserved regions, particularly Africa. |
|
Viability Gap Funding Scheme |
To provide grants to solar projects in Least Developed Countries and Small Island Developing States, easing financial barriers. |
|
Solar Data Portal |
It offers real- time data to inform investment decisions. |
|
International Solar Festival |
To foster global collaboration on solar solutions. |
|
Green Hydrogen Innovation Centre |
To explore synergies between solar energy and hydrogen. |
|
ISA Knowledge Series and World Solar Reports |
To promote research, insights, and market trends, positioning ISA as a leading advocate for solar energy worldwide. |
|
|
|

The first ISA project is expected to be in Cuba where auctions have taken place and a developer has been selected to set up a 60 MW plant.
|
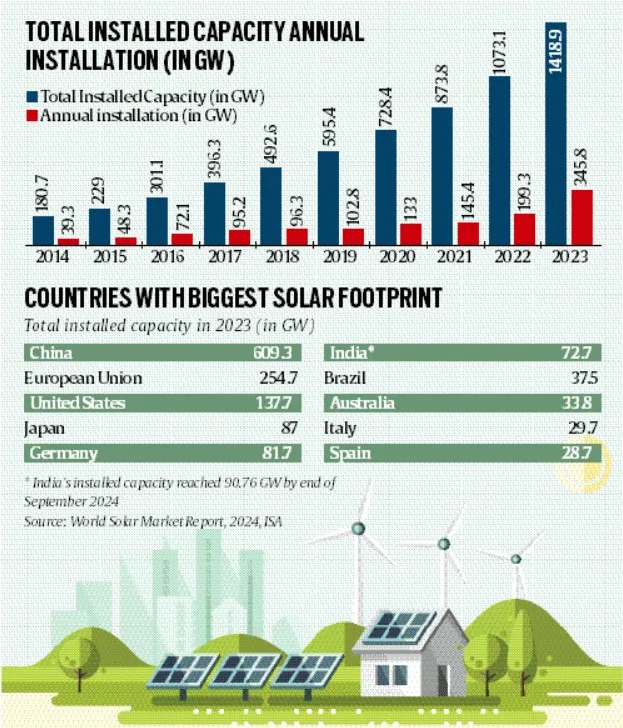
India’s Solar Sector |
|
References