Recently, Lok Sabha passed the Data Protection Bill, India’s 2nd attempt in framing a privacy legislation.
India does not have a standalone law on data protection. Use of personal data is regulated under the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000.
Personal data is defined as any data about an individual who is identifiable by or in relation to such data.
|
Penalty |
Reason |
|
Rs 200 crore |
Non fulfilment of obligations for children |
|
Rs 250 crore |
Failure to take security measures to prevent data breaches. |
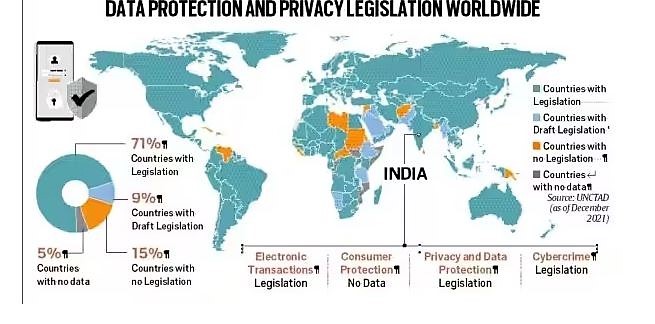
According to data from the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, 137 out of 194 countries have put in place legislation to secure the protection of data and privacy.
|
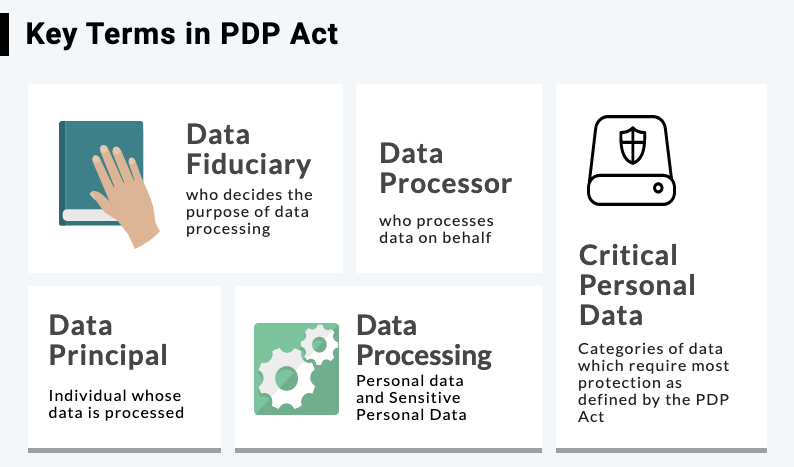
Right to data portability- The right to data portability allows data principals to obtain and transfer their data from data fiduciary.
Right to be forgotten- It refers to the right of individuals to limit the disclosure of their personal data on the internet. |
Models for data protection laws
What lies ahead?
References