7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
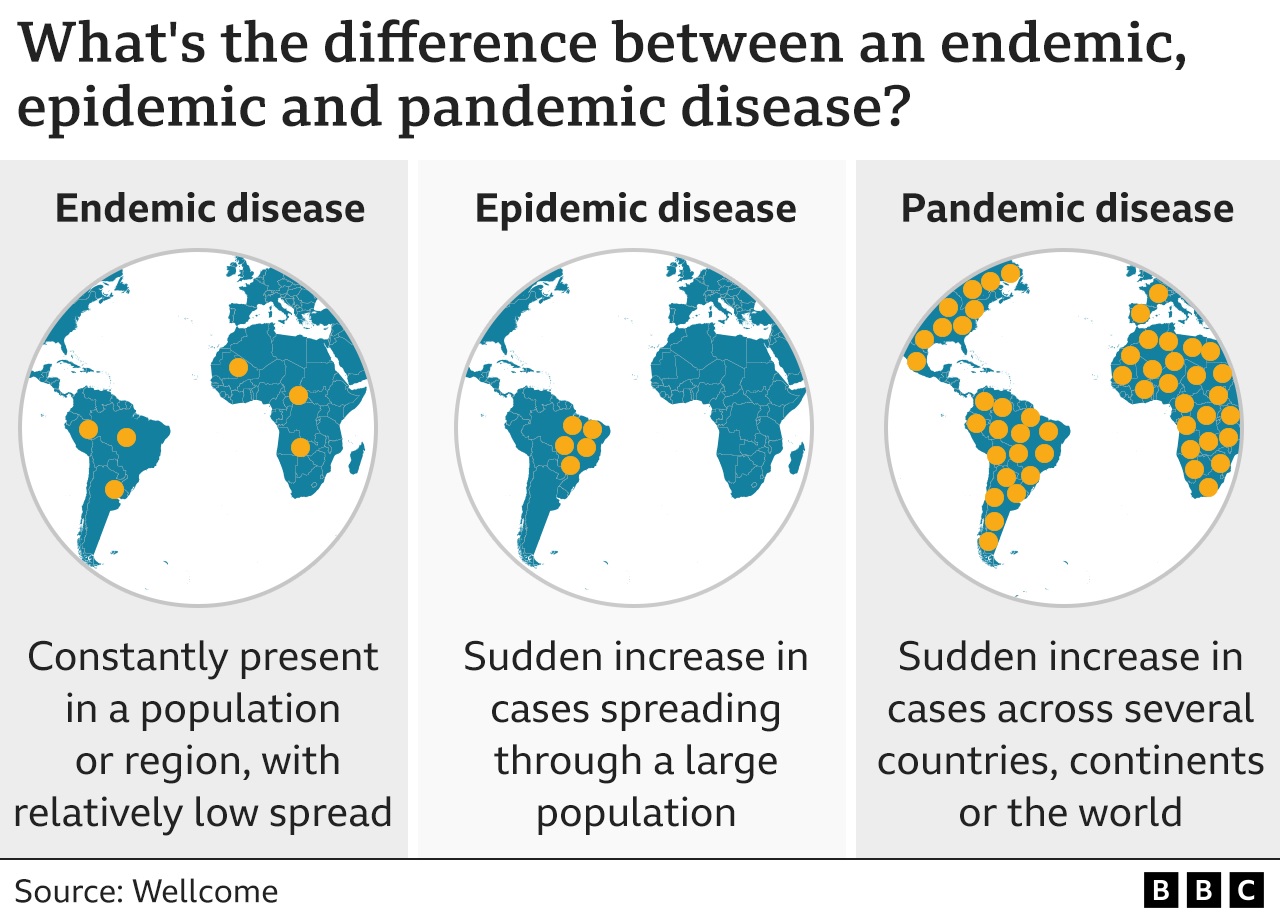
The UK has eased restrictions while new measures in California approach Covid-19 as being endemic.
The Alpha variant was first identified in the United Kingdom, Beta in South Africa, Gamma in Brazil, Delta in India and Omicron in southern Africa.
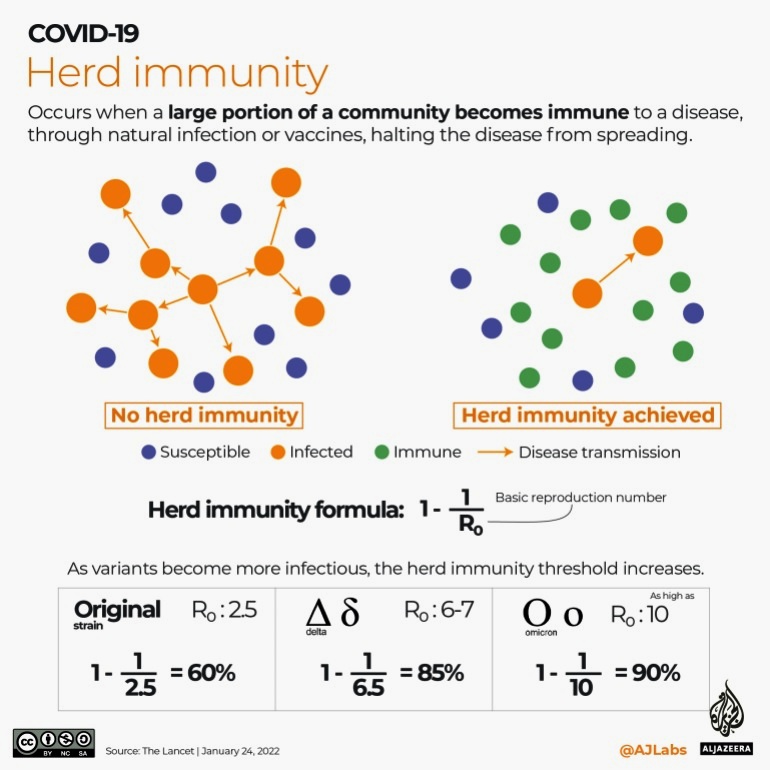
References