7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
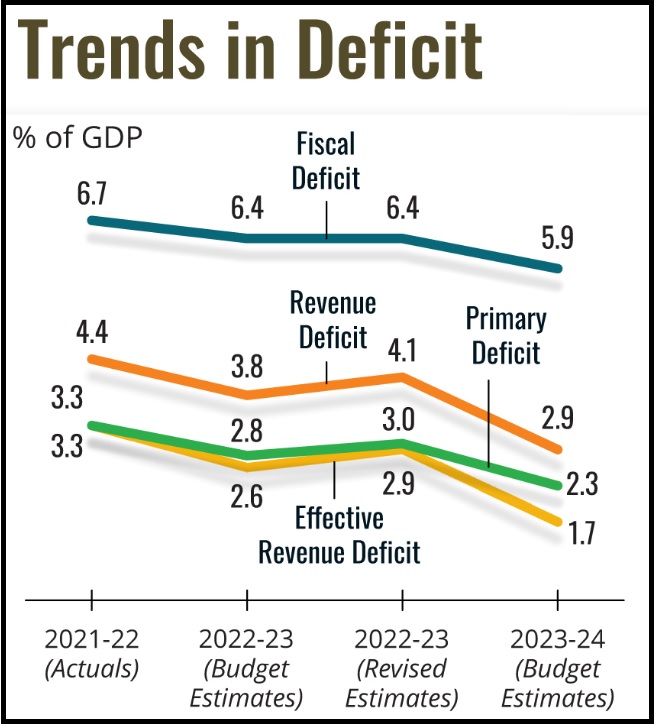
The 2023-24 Budget’s attempt to address the aspirations of different segments of society is a good effort in a difficult situation and the main focus is on fiscal consolidation.
To know about the summary of Budget, click here
What are the key facts of budget 2023-24?
References