Gold Monetization Scheme (GMS)
Prelims – Indian Polity and Governance, Current events of national and international importance.
Mains (GS III & II) – GS III (Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment) | GS II (Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation).
Why in the News?
Recently, the Ministry of Finance has decided to discontinue the Gold Monetization Scheme (GMS).
- Launched in – 2015.
- Objective – To mobilise idle gold held by households, trusts and various institutions of the country.
- To facilitate its use for productive purposes, and in the long run to reduce country’s reliance on the import of gold.
- It is revamped version of Gold Deposit Scheme (GDS).
- Deposit features
|
Types of deposits
|
Duration
|
Minimum Lock-in Period
|
Interest Rate
|
|
Short Term Bank Deposit (STBD)
|
1-3 years
|
Determined by banks
|
Determined by banks
|
|
Medium Term Government Deposit (MTGD)
|
5-7 years
|
3 years
|
2.25% p.a.
|
|
Long Term Government Deposit (LTGD)
|
12-15 years
|
5 years
|
2.50% p.a.
|
- Interest rate
- For MTGD & LTGD – They are decided by the government, in consultation with the RBI and borne by the Central government.
- Minimum deposit – 10 grams of raw gold (bars, coins, jewellery excluding stones and other metals).
- Maximum deposit – No limit for maximum deposit.
- Eligibility
- Resident Indians – Individuals, Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), Proprietorship & Partnership firms.
- Trusts – Mutual Funds/Exchange Traded Funds registered under Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- Companies, charitable institutions, Central & State Government or any other entity owned by Central or State Government.
Proposed changes for closure
- Reason for closure – Evolving market conditions and performance of the scheme.
- Changes – Discontinuation of MTGD and LTGD, including renewal of existing deposits.
- Existing deposits of MTGD and LTGD will continue till maturity.
- Since short-Term Deposits (STBD) are under the ambit of banks in the scheme, it can continue at the discretion of individual banks based on the commercial viability as assessed by them.
Gold Monetisation Scheme (GMS) is the 2nd gold scheme to face closure by the government after sovereign gold bonds.
References
- The Indian Express| Government Ends Gold Monetization Scheme
- RBI| Gold Monetization Scheme (GMS), 2015
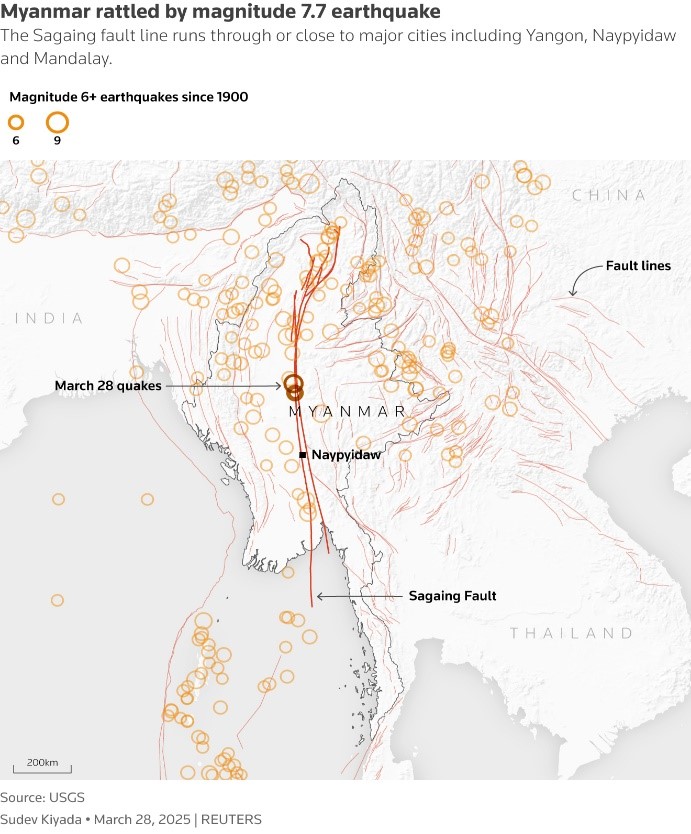
Causes of Myanmar’s Earthquake
Prelims – Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and the World.
Current events of national and international importance.
Mains (GS I & III) – GS I (Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc.) | GS III (Disaster and disaster management).
Why in the news?
India’s National Centre for Seismology says soil liquefaction caused severe damage in the recent earthquake that stuck in Myanmar.
- Earthquake – It is the shaking of the earth's surface caused by a sudden release of energy within the earth's crust.
- Epicentre – Mandalay in Myanmar
Focus or Hypocenter is the point within the Earth where an earthquake rupture starts. Epicenter is the point at the surface of the Earth above the focus.
- Cause of earthquake – Mainly due to Sagaing Fault,
|
Sagaing Fault
|
- It is a major fault line located 1,200 km east of the Indo-Burma subduction zone.
- Geography – To the east of the Sagaing Fault is the Sunda Plate.
- The Fault is the partitioning between the Myanmar plate and the Sunda plate.
- Concept – It is a ’strike-slip’ fault, which means that the Indian and Sunda landmasses are moving horizontally against each other which releases a lot of energy.
|
- Major causes for damage
- Resonance Effect – The natural frequency of a structure matches with the frequency of seismic waves, causing amplified vibrations.
- Soil liquefaction.
Thailand's capital Bangkok, which is more than 1,000 km away from the epicentre suffered significant damage as the rupture's direction was towards it.
|
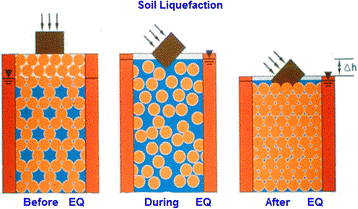
Soil liquefaction
|
- It is a phenomenon that occurs when saturated, loose soil loses its strength and behaves like a liquid due to intense seismic shaking.
- Conditions – It usually occurs in places with loose, wet soil like sandy areas near rivers or the coast.
- Concept – When the earthquake shakes the ground, the water between the soil particles pushes them apart, making the soil lose its strength.
- Consequences – As a result, buildings, roads and other structures may sink, tilt or collapse.
EQ- Earthquake
|
National Centre for Seismology is the nodal agency involved in monitoring seismic activity across the country with the help of National network consisting of 166 stations. It works under Ministry of Earth Sciences and are aimed at better earthquake monitoring, early warning systems, and research into seismic activity.
Reference
The Hindu| Myanmar-Thailand Earthquake
Related News - Earthquake
Sarhul Festival
Prelims – Social Geography of India
Mains (GS I) - Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
Why in News?
Adivasis in Jharkhand and the larger Chhotanagpur region will welcome the new year and the spring season with the Sarhul festival on Tuesday.
- Sarhul – It literally means “worship of the Sal tree” and is among the most revered Adivasi festivals.
- Nature worship - Sal trees (Shorea robusta) are venerated in Adivasi tradition.
- Sarna faith - Jal (water), jungle (forest), jameen (land) — these three aspects of nature form the core of the Sarna faith.
- Sarna Maa – The Sal trees are seen as the abode of Sarna Maa, the deity protecting the village from inclement natural forces.
- Union of Sun and Earth – The festival celebrates the symbolic union of the Sun and the Earth.
- A male priest from the village (pahan) plays the role of the Sun, while his wife (pahen) becomes the Earth.
- Sowing season - Only after the rituals are completed, Adivasi folk begin ploughing their fields, sowing their crop, or entering the forest to gather produce.
- Tribes - Sarhul has been celebrated by tribes such as the Oraon, Munda, Santal, Khadia, and Ho, with unique names for the festival and particular ways of celebrations.
- Sarna Sthals - These are communally protected “sacred groves” and can be found near villages across Chotanagpur, including Jharkhand, parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and Bihar.
- Sarna flags - In the lead up, homes and Sarna Sthals are lined with triangular, red and white Sarna flags.

- Three-day festival - The main rituals happen on day two of the three-day festival at Sarna Sthals.
- First day event - On the first day of Sarhul, the village’s pahan, who observes a rigorous fast, fetches water for the ceremonies, houses and Sarna Sthals are cleaned, and Sal flowers gathered for rituals.
- Second day event - On the next day, the main rituals take place at the Sarna Sthal.
- The deity is presented with Sal flowers, and a rooster is sacrificed.
- Villagers seek prosperity, safety, and a good harvest.
- Holy water is then sprinkled across the village, with performances of traditional songs and dances such as Jadur, Gena and Por Jadur.
- Later, young men head to nearby ponds and rivers and participate in ceremonial fishing and crab-catching to gather food for the ceremonial feast.
- Third day event - The final day is marked by a grand community feast, in which people share handia (rice beer) and enjoy a variety of delicacies.
- The festival ends with the pahan’s blessings and the villagers praying.
- Evolution - Over time, Sarhul evolved from being a hunting-centred tradition to one that revolves around agricultural processes, reflecting the evolving lifestyle of Adivasis in Chhotanagpur.
- Celebration in other countries - During the 19th and early 20th centuries, when tribes such as the Munda, Oraon, and Santal were sent to faraway places as indentured labour, Sarhul traveled with them.
- Today, the festival is celebrated in locations ranging from the tea gardens of Assam to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Bhutan.
- Sarhul procession - In the 1960s, Adivasi leader Baba Karthik Oraon, who advocated for social justice and the preservation of tribal culture, began a Sarhul procession from Hatma to the Siram Toli Sarna Sthal in Ranchi.
- Siram Toli - In the past 60 years, festive processions have emerged as a crucial part of Sarhul, with the Siram Toli site becoming a major point of convergence for processions.
- Political identity – The procession and gathering has also made Sarhul increasingly political, and an occasion to assert the Adivasi identity.
- Separate religion - Adivasis following the Sarna faith have been demanding the inclusion of a Sarna religion column in the census.
At present, under the census, there are codes for only six religions: Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism and Jainism.
Reference
The Indian Express | Sarhul
2nd WHO Conference on Air Pollution and Health
Prelims – General issues on Environmental ecology, Climate Change; Current Events of International Importance.
Why in News?
Recently, the second World Health Organisation (WHO) conference on air pollution and health was concluded.
- Conference location - Colombian city of Cartagena
- Organizers - Jointly organized by WHO and the Government of Colombia
- Participants - Over 700 participants including government representatives, U.N. agencies, civil society, scientists, and health societies.
- Goal - A shared goal to reduce the health impacts by 50% by 2040 was agreed upon to save millions of lives every year.
- Impact of Air Pollution - Air pollution claims more victims than violence itself and poisoning our air costs lives in silence.
- Participant’s commitments - More than 50 countries, cities and organisations announced major commitments to tackle air pollution and safeguard health.
- India’s commitment - India has committed to supporting the health sector with actions in alignment with the National Clean Air Programme to reduce the health impacts of air pollution by 2040.
- It also committed to strengthen air pollution and noncommunicable disease surveillance, promote cleaner cooking energy, particularly for vulnerable populations, and support clinicians in protecting at-risk patients.
National Clean Air Programme aims at 40% reduction in particulate matter by 2026.
The acceptable annual standard for PM2.5 is 40 micrograms per cubic metre and PM10 is 60 microgram per cubic metre.
- Spain’s carbon-neutral health-care system - Spain assured that they are “committed to achieve” a carbon-neutral health-care system by 2050 through emission reduction, multi-sectoral collaboration and promoting innovation.
- Forum for International Cooperation on Air Pollution (FICAP) - The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland reaffirmed its commitment to tackling air pollution by chairing the Forum and publishing an Air Quality Strategy.
The purpose of the Forum for International Cooperation on Air Pollution (FICAP) is to promote international collaboration towards preventing and reducing air pollution to improve air quality globally.
It is co-lead by Sweden and the United Kingdom and open to participation from all regions, countries, NGOs and IGOs, researchers and industry associations.
- C40 cities commitment - On behalf of the co-chairs of C40 cities, representing almost 100 of the world’s biggest cities, the Deputy Mayor of London assured supporting WHO’s 2040 target and roadmap.
C40 is a global network of mayors of the world’s leading cities that are united in action to confront the climate crisis. (Indian Cities – Chennai, Bengaluru, Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Delhi)
- Clean Air Fund (CAF) - It committed to continuing to support WHO in demonstrating the benefits of life-saving clean air actions.
- It also committed to allocate an additional US$ 90 million over the next two years for climate and health efforts.
The Clean Air Fund is a philanthropic initiative with a mission to tackle air pollution around the world and brings together funders, researchers, policy makers and campaigners to find and scale solutions that will provide clean air for all.
Reference
The Hindu | WHO conference
Childhood Mortality and Stillbirth
Prelims – Economic and Social Development.
Mains (GS II & III) – GS II (Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources) | GS III (Inclusive growth and issues arising from it).
Why in news?
The United Nations Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (UNIGME) in its recent report has lauded India for its effort in mitigating childhood mortality and stillbirth.
- The United Nations Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (UNIGME) recently published its "Levels and Trends in Child Mortality" report.
- It is an annual report that provides data for 195 countries.
- Child mortality – It is also known as under-five mortality rate.
- It is the number of children who die by the age of 5 years, per 1000 live births.
- Stillbirth – A baby who dies after 28 weeks of pregnancy, but before or during birth, is classified as a stillbirth.
Key findings of the report
- While the world has made progress in reducing child mortality, the rate of improvement is slowing down.
- Millions of children still die from preventable causes, often due to unequal access to healthcare, nutrition, and protection, especially in vulnerable areas.
- India – India is on 7th position among the top 10 countries in highest reduction of stillbirths in the range of 60-70%.
- Between 2000 and 2023, India achieved a 70% decline in the under-five mortality rate and 61% decline in the neonatal mortality rate.
- Stillbirth in India is reduced 60.4% in between 2000-2023 in comparison to 37% global reduction.
|
United Nations Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (UN IGME)
|
- UN IGME was formed in 2004 to share data on child mortality, improve methods for child mortality estimation.
- It also reports on progress towards child survival goals and enhance country capacity to produce timely and properly assessed estimates of child mortality.
- UNIGME is a collaborative effort led by:
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF),
- World Health Organization (WHO),
- The World Bank Group and
- The United Nations Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
- UN IGME updates its child mortality estimates annually after reviewing newly available data and assessing data quality.
- The web portal contains the latest UN IGME estimates of child mortality at the country, regional and global levels and the data used to derive them.
|
References
- Business standard | childhood mortality and stillbirth
- UN IGME | About UN IGME
|
One Liners 02-04-2025
|
|
History, Art and Culture
|
|
Odisha Foundation Day or Utkal Divas
The people of Odisha on Utkala Dibasa, celebrating the state's formation.
- Celebrated on – April 1st , 2025, marking the 88th anniversary of Odisha's statehood, achieved in 1936.
- From Bengal Presidency to Statehood – Prior to 1936, Odisha was part of the Bengal Presidency, alongside Bihar and Jharkhand.
- The movement for a separate state gained momentum in the early 1920s.
- Prominent leaders in the Statehood Movement – Madhusudan Das, Utkalmani Gopabandhu Das, and Fakir Mohan Senapati.
|
|
Geography
|
|
Chicken's Neck Corridor
Bangladesh has invited China to invest in a river conservation project near the Chicken's Neck Corridor, raising strategic concerns for India.
- Chicken's Neck or Siliguri Corridor – It is a narrow land strip in West Bengal, crucial for connecting India's mainland to its northeastern states.
- Link to northeastern states – Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, and Sikkim, vital for their integration with the rest of the country.
- Bordered by – Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
- Strategic importance – It is essential for military movement and supply, and any disruption could isolate India's northeast, posing a severe security threat.
- China's role – Its proximity to the India-China border, especially the Chumbi Valley, where China has military infrastructure.
|
|
Social Issues
|
|
Bodh Gaya Temple Act Protest
Buddhist monks, under the All-India Buddhist Forum (AIBF), have been protesting since February 2024, demanding the repeal of the Bodh Gaya Temple Act (BTA), 1949.
- BTA, 1949 – It established an 8-member management committee to oversee the Bodh Gaya Temple's administration.
- Management committee composition – The Act mandated equal representation for Hindus and Buddhists.
- District Magistrate (DM) – Ex-officio chairperson, historically from the Hindu community, created a perceived Hindu majority in the committee.
- Hindu control – In 1590, a Hindu monk established the Bodh Gaya Mutt, resulting in Hindu control over the temple's administration.
|
|
Polity & Governance
|
|
NITI NCAER States Economic Forum Portal
NITI NCAER States Economic Forum portal was launched recently.
- About – It is a comprehensive repository of data on social, economic and fiscal parameters, research reports, papers and expert commentary on State Finances for a period of about 30 years (1990-2023).
- Launched on – April 1, 2025.
- Launched by – NITI Aayog and the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER).
- 4 main components – State Reports, Data Repository, State Fiscal and Economic Dashboard, and Research/Commentary.
|
|
Silk Samagra-2 Scheme
The government is implementing the Silk Samagra-2 scheme (2021-26).
- Objective – To boost India's sericulture industry.
- Financial assistance – It provides financial aid to states for various interventions including, Nursery development, silkworm rearing, chawki rearing centers, and post-cocoon activities like reeling and weaving.
- Beneficiary coverage – Both pre and post-cocoon activities.
- Regional support to – Specifically, Andhra Pradesh & Telangana for beneficiary-oriented projects in the last 3 years.
|
|
Sahkar Taxi
The Indian government will launch Sahkar Taxi.
- About – It is a cooperative-based taxi service, to compete with existing ride-hailing platforms like Ola and Uber.
- Aim – To provide a viable, driver-centric alternative, fostering economic empowerment and addressing market gaps.
- Vehicle types – 2-wheeler, auto-rickshaw, and 4-wheeler taxis.
- Direct driver benefits – It will channel all profits directly to drivers.
- Cooperative insurance for drivers – It will include a cooperative insurance company, providing drivers with essential insurance coverage.
|
|
International Relations and Issues
|
|
Exercise Tiger Triumph IV
Exercise Tiger Triumph IV will occur on the Eastern Seaboard from April 2025.
- It is the 4th edition of bilateral India-US humanitarian and disaster relief exercise, will took place in Visakhapatnam.
- Aim – To enhance interoperability and develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for joint HADR operations, establishing a Combined Coordination Center (CCC).
|
|
Environment
|
|
Siberian Tiger/Amur Tigers
A recent study in Oryx highlights the increasing incidents of tigers killed in road, posing a significant threat to Amur Tiger survival.
- Scientific name – Panthera tigris altaica.
- They're the largest tiger subspecies, adapted to cold climates with thick fur and a light coat.
- Habitat and Distribution – They primarily inhabit eastern Russia's birch forests, with limited presence in China and potentially North Korea.
- Population – Estimates place their population at 265-486 in Russia (2022).
- Threats – Poaching and human-wildlife conflict.
- Conservation status in IUCN – Endangered.
|
|
Security
|
|
Operation Brahma
India recently launched the Operation Brahma, to provide humanitarian aid to Myanmar.
- Objective – To provide humanitarian aid after a devastating 7.7-magnitude earthquake struck Myanmar.
- Earthquake impact & response – It is caused widespread destruction and over 1,600 fatalities in Myanmar and neighboring Thailand, prompting India's swift response.
- Naval support & aid delivery – INS Satpura and INS Savitri were dispatched, carrying 40 tonnes of humanitarian aid to Yangon, ensuring the timely delivery of essential supplies.
|
|
Miscellaneous
|
|
International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC)
IRFC has recently launched a $100 million appeal to aid victims of the recent devastating Myanmar earthquake.
- The IFRC unites 192 Red Cross and Red Crescent societies, mobilizing millions of volunteers for humanitarian aid.
- Founded in – 1919 and based in Geneva.
- Aim – To assist vulnerable populations by coordinating international emergency response to disasters, including natural, man-made, and health crises, and strengthening community resilience.
- Funding and Partnerships – The IFRC relies on voluntary contributions from various sources and collaborates with the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), which focuses on humanitarian law and conflict aid.
|
