Recent study on PM2.5 in North India
Why in News?
A recent study published in the journal Nature Communications has investigated the sources and health impacts of PM2.5 in Northern India, particularly in the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
PM2.5 describes fine inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers and smaller.
- The study has examined PM2.5 composition and oxidative potential, a key indicator of its health risks.
- Comparative analysis shows that the oxidative potential of PM2.5 in Indian cities is among the highest globally, exceeding levels in Chinese and European cities by up to five times.
Oxidative potential (OP) is a metric that measures the ability of particulate matter (PM) to create reactive oxygen species (ROS).
- Samples collected sites - Urban and roadside locations in Delhi, rural and industrial peripheries, and a suburban site in Kanpur.
- Causes - Local emission sources – Local sources and atmospheric processes dominate particulate matter pollution.
- In Delhi, PM2.5 is dominated by ammonium chloride and organic aerosols from vehicular emissions, residential heating, and fossil fuel oxidation
- Outside Delhi, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, and biomass-burning-derived organic aerosols are more prominent.
- Incomplete Combustion - PM2.5 oxidative potential is primarily influenced by organic aerosols from incomplete combustion of biomass and fossil fuels, particularly from traffic, residential sources.
- It is observed across all locations, emphasizing that inefficient local combustion is a major contributor to PM2.5-related health risks.
- Vehicular tailpipe emissions - Hydrocarbon-like organic aerosols originate from fresh vehicular tailpipe emissions.
- The study found that the highest average hydrocarbon-like organic aerosols concentrations (8 micrograms per metre cube) were recorded at the urban roadside site in Delhi.
- Hydrocarbon-like organic aerosols are primarily from traffic and contribute up to 20% of total organic aerosols mass with higher relative contributions in the warm season.
- From 20%, the contribution from traffic can increase to 40% at urban roadside.
- In all, hydrocarbon-like organic aerosols constitute 50% of the total fossil (coal, petrol, diesel) organic aerosols.
- Cow dung combustion - During winter for heating and cooking contributes to cold-season primary organic aerosols.
- The cold-season primary organic aerosols are highly elevated during the night and exhibit spatially homogeneous contribution.
- Also, concentration of cold-season primary organic aerosols during cold weather are up to 10 times higher than during warmer weather.
- Urban oxygenated organic aerosols are affected by both fossil emissions from vehicle exhausts and non-fossil emissions from cooking, and have similar concentration levels across seasons.
- While hydrocarbon-like organic aerosols and urban oxygenated organic aerosols are especially important inside Delhi, cold-season oxygenated organic aerosol forms outside Delhi.
- The study provides crucial insights for policymakers to design effective air quality control strategies focused on reducing primary emissions from incomplete combustion.
Reference
The Hindu | Health effects of PM2.5 in northern India
Ruellia elegans
Why in News?
A new study has flagged the threat to native biodiversity because Ruellia elegans, an invasive plant from Brazil, recorded for the first time in Assam’s oil town Digboi.
- It is a flowering plant native to Latin America, invasive to India.
- It is commonly known as the Brazilian petunia, Christmas pride, elegant Ruellia, red Ruellia, and wild petunia.
- It derives its name from its pleasing appearance or elegance.
- Appearance – It appears with bright red trumpet shaped flowers that appear on 6 to 8 inch wand-like stems.
- The upper petals tend to flare out and back, while the lower one curls out and downward.
- It forms a 12 inch high by 24 inch in diameter mound of soft green, semi-fuzzy foliage.
- Habitat - Predominantly thriving in wet tropical biome.
- The plant tolerates a light frost, but dies back at about 28 degrees.
- Life Cycle – Annual.
- Soil Texture - High Organic Matter, Loam (Silt).

- Conservation status - Not assessed.
- Threats - Bacterial leaf spots, fungal leaf spots, rust, root rot.
- The Brazilian flowering plant was introduced in the Andaman Islands, apart from Jamaica and Puerto Rico.
- It is one of 4 invasive species of the Acanthoideae sub-family in India, the others being Ruellia ciliatiflora, Ruellia simplex, and Ruellia tuberosa.
India has 6 native species of Ruellia namely, beddomei, ciliata, malabarica, patula, sibua, and sivarajanii.
References
- The Hindu | Ruellia elegans
- NCSU Edu | Ruellia elegans
Survey of India’s river dolphins
Why in News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently released the results of the first-ever comprehensive population estimation of riverine dolphins – Gangetic and Indus dolphins, done in India.
- Done by - Wildlife Institute of India
- Nodal Ministry - Union Environment Ministry.
- Duration - 2021 and 2023.
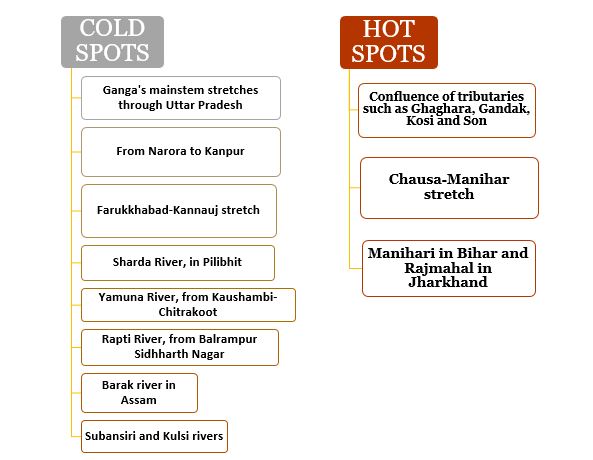
- Coverage - It covered the main channels and tributaries of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers, as well as the Beas River in Punjab.
- The survey spanned Ganga and its tributaries in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
- Brahmaputra including its tributaries Subansiri, Kulsi, Beki, Kopili, and Barak were surveyed.
- Key Findings - It estimated an average of 6,324 Gangetic dolphins, ranging from 5,977 to 6,688. The survey only found three Indus River dolphins in the Indus basin, all in the Beas River in Punjab.
- It thus estimated an average of 3,275 dolphins on Ganga’s main stem, 2,414 in its tributaries, 584 in Brahmaputra’s main stem and 51 in its tributaries.
- In Beas, it only found 3 Indus River Dolphins, considered a separate species from the Gangetic dolphins.
- The highest number of Gangetic dolphins, 2,397, was found in Uttar Pradesh.
- This was followed by 2,220 in Bihar, 815 in West Bengal, 6235 in West Bengal, 162 in Jharkhand, 95 in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh, and three in Punjab.
- Methodology - River dolphins live in opaque, turbid waters and briefly appear on the surface, making any estimates of their population tricky.
- According to the population estimation report, dolphins surface only for 1.26 seconds and dive for 107 seconds.
- A combination of visual and acoustic surveys is used. The acoustic survey uses multiple underwater microphones or hydrophones to capture ‘dolphin clicks.’
- Echolocation - Dolphins, being functionally blind, navigate by making clicking sounds that travel through water and bounce back after hitting objects. This process is called echolocation.
- Hydrophones record underwater dolphin clicks to counter observer error and reliably triangulate dolphin occurrence.
- Since multiple hydrophones are used, they can pick up clicking sounds made by different individuals.
- For deep and wide channels, the double observer method is used, where two teams positioned on different decks cover different angles around the vessel on its left and right flank.
- These teams scan for dolphins surfacing around them as the boat travels at 8-10 km/hour.
- This allows for efficient detection and helps avoid double counting individual dolphins, given that the boat travels faster than the dolphins.
- Tandem method - Used for channels less than 600 metres wide and 3 metres deep, while
- A single boat method is used for channels with a width smaller than 300 metres and a depth lower than 2 metres.
Reference
The Indian Express | Comprehensive survey of India’s river dolphins
Hearing Problem in India
Why in News?
World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that by 2050, nearly 2.5 billion people worldwide may experience hearing loss, with over 700 million needing rehabilitation.
- Global status - The global average indicates that one in 1,000 newborns is born with significant hearing loss, the number is twice as high in India.
- Alarmingly, a significant percentage of those affected are children aged 0 to 14 years.
- WHO warns that the prevalence of hearing loss increases with age, among those older than 60 years, over 25% are affected by disabling hearing loss.
- Hearing loss among older adults mirrors the progression of cataracts, here, it is sound, not sight that fades away.
- Status in India - Around 63 million people, or 6.3% of India’s population live with significant auditory impairment.
- A recent study revealed that 5% of students had undiagnosed hearing loss, often thought to be slow learners or as having learning disabilities.
- In Tamil Nadu especially, the burden is even higher than the Indian average, 6 in every 1,000 newborns affected.
- Contributing factors - Congenital infections like rubella, neonatal complications such as low birth weight, and birth injuries.
- Treatable conditions like fluid buildup in the ears due to recurring colds or chronic infections often go unchecked.
- For young adults, hearing loss stems less from birth-related causes and also from lifestyle choices.
- The overuse of headphones, Bluetooth devices, and mobile phones.
- Recreational noise exposure from loud concerts, home theatre systems, and high-volume phone calls further pushes people beyond safe noise levels.
National Programme for Prevention and Control of Deafness (NPPCD), an initiative of the Union Health Ministry, introduced free hearing tests, awareness campaigns, and support for cochlear implants in children.
|
World Hearing Day
|
- It is a campaign held each year by Office of Prevention of Blindness and Deafness of the World Health Organization.
- Hosted on - March 3.
- Aim - To raise awareness on how to prevent deafness and hearing loss and promote ear and hearing care across the world.
- Theme, 2025 - "Changing mindsets: empower yourself to make ear and hearing care a reality for all!"
|
Reference
The Hindu | World Hearing Day
RBI on Foreclosure Charges
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) floated a consultation paper seeking to waive foreclosure charges, and prepayment penalties, on loans taken by micro and small enterprises (MSEs).
- Recent Changes - RBI has proposed that banks and NBFCs must not levy foreclosure charges or prepayment penalties on loans taken at floating rates by MSEs for business purposes.
- At present, the provision only exists for loans taken by individuals for purposes other than business.
- The proposed regulation thus extends the purview of the guideline.
- Eligibility - This shall apply to all MSE borrowing up to Rs.7.5 crore
- Barring an exception for Tier 1 and Tier 2 Primary (Urban) Co-operative Banks and base layer NBFCs, that is, those with asset sizes of below Rs.1,000 crore.
- RBI also underlines that banks and NBFCs cannot stipulate any minimum lock-in period for the proposed guidelines to become applicable.
- Furthermore, it underlines that regulated entities cannot levy any retrospective charges which were waived off earlier and/or not disclosed in advance to the borrowers.
- Objectives - The primary objective of the proposed measures is to provide for easy and affordable financing to MSMEs.
- The waiver would bring more borrowers into the formal system (of credit).
- It mitigates the risk of hidden charges and offers better ability for MSMEs to plan their cash flows and incentivises borrowers to repay.
- The proposed measures are meant to help small businesses to clear their debts without penalties.
Reference
The Hindu | RBI on foreclosure charges
|
One Liners 05-03-2025
|
|
Bilateral Relations
|
|
India-Japan S&T Collaboration
- Indo-Japan S&T cooperation was formalized through Inter-Governmental Agreement signed in 1985.
- Indo-Japan Joint S&T Committee – Is the apex body which provides vision and direction to the cooperative S&T activities.
- The committee is Co-chaired by Department of Science & Technology (DST) India and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MoFA), Japan.
- Celebrated on – India’s National Science Day (28 Feb, 2025) at Indian Embassy, Tokyo in Japan.
- Collaboration in – Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning, Quantum Technology, and Space.
|
|
Economy
|
|
India's Research and Development (R&D) Spending
- R&D funding – Led to India’s Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD) more than doubling in the last decade (i.e Rs 60,196 cr-Rs 1,27,381 cr).
- It is shaping the future economy in artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and quantum computing.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat – It is not only investing in research but also ensuring that these innovations are seamlessly transitioned from labs to industries, strengthening the foundation of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
|
|
Navratna Status
- Navratnas – It is a 2nd category of the central government-owned ‘Ratna’ companies, placed between the Maharatnas and the Miniratnas based on criteria.
- Navratna status in Indian Railways (IR):
- Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC) – 25th
- Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC) – 26th
- IR CPSEs – Totally 12, out of which 7 are listed Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) have Navratna status.
|
|
Agriculture
|
|
Central Plantation Crops Research Institute (CPCRI)
- Established in – 1970, under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Headquarters – Kasaragod district, Kerala.
- It is one of the agricultural research institutes in the National Agricultural Research System (NARS).
- It is mandatory for the Institute to conduct research on coconut, arecanut, Palmyrah and cocoa.
|
|
Environment
|
|
Vantara
- About – It is a large-scale animal (wildlife) rescue center, that operates through caves, conservation, and rehabilitation measures.
- Located in – Jamnagar, Gujarat.
- Established by – Reliance Industries and Reliance Foundation.
- Area – 3,000 acres.
- Fauna – It is home to over 2,000 animals across 43 species.
|
|
Carbon Intensity (CI)
Recently, China lowered its carbon intensity by 3.4% in 2024, by missing its target of 3.9%.
- About – It is a useful way to measure how much carbon a particular sector is emitting and how it has increased or decreased over time.
- Measurement – An entire country’s carbon intensity can be calculated by dividing the growth in GDP per capita by the amount of carbon dioxide emitted.
|
|
Science
|
|
Agentic AI
- About – It is meant to automate tasks for users so that they do not have to prompt the systems to take actions for them.
- It has the potential to be the next multi-billion business.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – It forms a new group to focus on agentic Artificial Intelligence (AI).
|
|
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
- SMR – It is an advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW (e) per unit.
- Deployed in – Industrial zones, remote areas, and hard-to-abate sectors like cement and steel manufacturing.
- India’s aim – To develop at least 5 indigenously SMRs by 2033.
|
|
Miscellaneous
|
|
Penshurst Estate
- Established in – 1875.
- Located in – Peerumade hills of Idukki, Kerala.
- It is Kerala’s 1st commercial tea plantation industry that has reached a historic milestone of 150 years.
- FY2023-24 – It was ranked 1st in South India for tea productivity per hectare, yielding 4,735 kg per hectare.
|
|
Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2025
- About – It is the world’s biggest mobile industry trade show.
- Location – Barcelona, Spain.
- Agenda – It’s the place where leaders of business, nations, and startups come together to set the agenda for the year ahead.
- Tech and telecom companies gearing up to launch new smartphones, AI hardware, and concept devices.
|
