7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Dragon Capsule
Hammer Missile
Munitions and their origins
Ammonium Nitrate
Nitrogen di-oxide
NGT order on ground water extraction
Section 5 of Environment Protection Act
Hoolock Gibbons
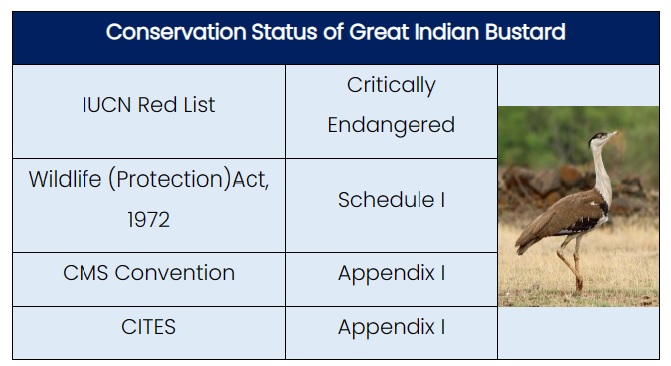
Source: Down to Earth, the Hindu, Times of India