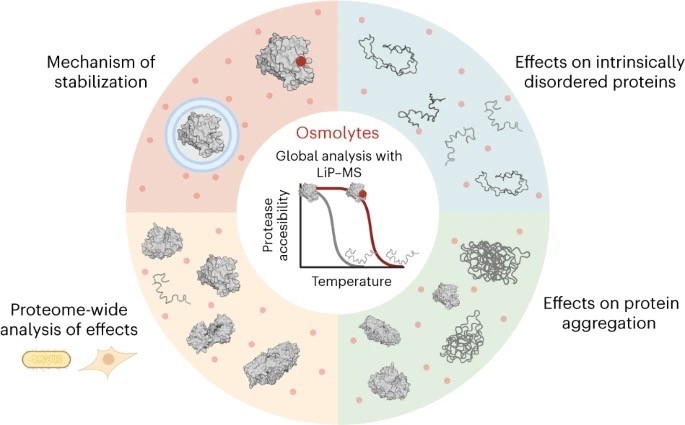
Recent research reveals that small molecules known as osmolytes help proteins stay stable and functional under stress.
Reference
The extended Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan has been recently launched by the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW).

PMSMA's ‘I Pledge For 9’Achievers Awards 'was initiated to recognize the contribution of private sector doctors who volunteered for the PMSMA scheme.
References
The central government is implementing the National Plan for Conservation of Aquatic Ecosystems (NPCA) to conserve and manage wetlands nationwide.
|
‘Wetlands Rejuvenation’ programme |
|
Reference
PIB | National Plan for Conservation of Aquatic
The scientists have identified major natural variations in rice nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), along with key traits and genes linked to this efficiency.
|
NUE rice varieties |
|
India is a signatory to the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (2022), which mandates countries to halve their nutrient waste from all sources by 2030.
Reference
Down to Earth | Rice nitrogen use efficiency