7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Impact of Energy Efficiency Measures Report
Perform, Achieve and Trade Scheme
Standards &Labelling Programme
Products under voluntary labelling
UJALA Programme
Demand Side Management Programme
Bureau of Energy Efficiency
Project CARD
Click here to know more about Covid-19 Testing
Luhman 16A
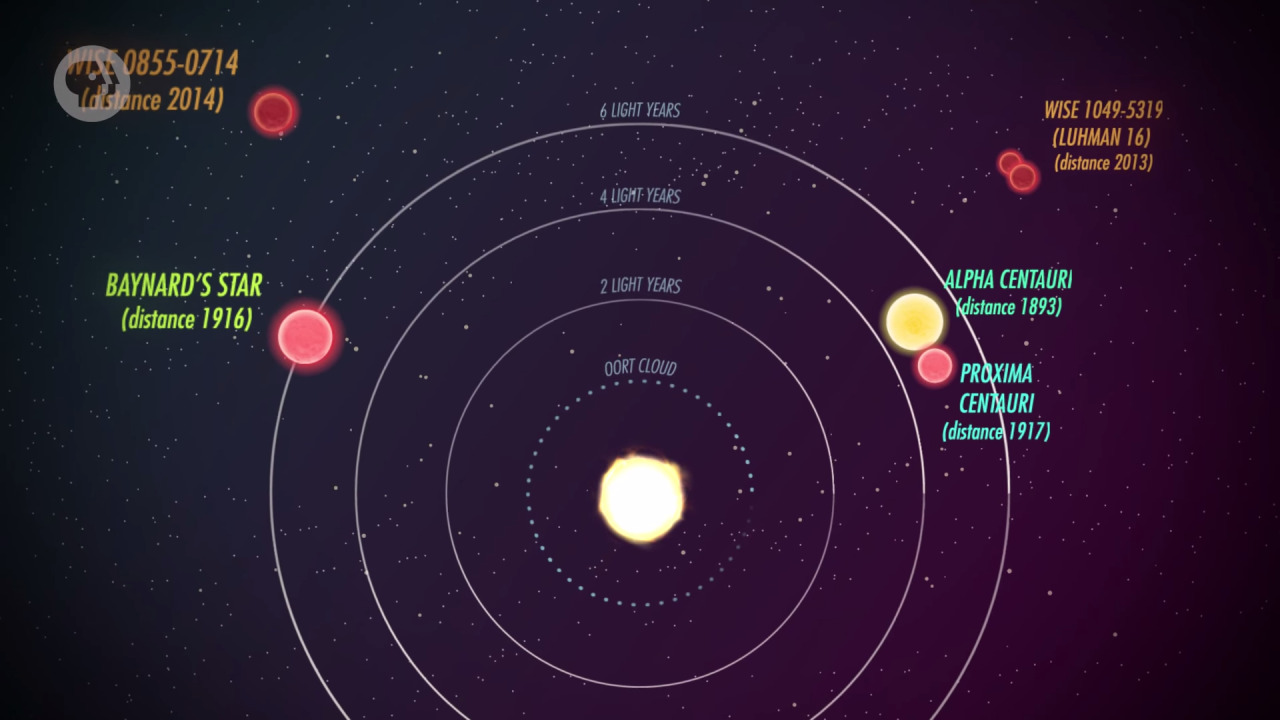
Brown Dwarfs
Tiger
Tiger Census
Sundarbans
Project Tiger
National Tiger Conservation Authority
Styrene Gas
Source: PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Economic Times