7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
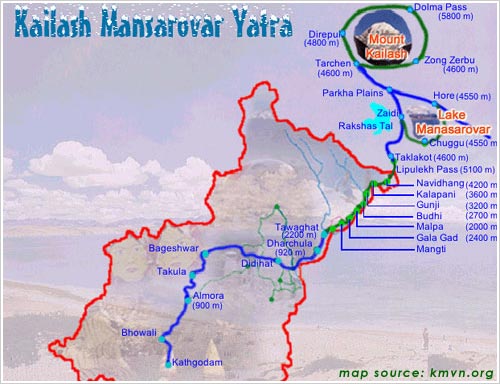
Kailash Mansarovar
Mutual Agreement Procedure (MAP)
Currency derivatives
GIFT City
International Financial Services Centre (IFSC)
India INX
Safeguards against Chemical Disasters in India
Chemical Hazards in India
Prime Minister’s Research Fellowship Scheme (PMRF)
Source: PIB, News on Air, the Hindu, Indian Express