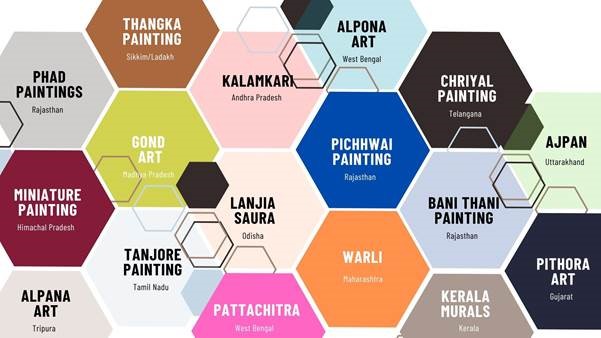
Recently, the Ministry of Culture launched Project PARI at the 46th Session of the World Heritage Committee Meeting in Delhi.
|
World Heritage Committee (WHC) |
|
References
Lalit Kala Akademi | Project PARI
Recently, the National Commission of Minorities held a meeting with states and Union Territories to discuss the implementation of the Anand Marriage Act.
|
National Commission for Minorities |
|
References
Recently, a team of scientists have traced the effect of plasma composition on dynamics of astrophysical jets from celestial bodies.
Reference
Recently, the Union Cabinet of India approves to sign of the Biodiversity beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement.
|
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) |
|
References