Evolution of the Tabla
Why in News?
Recently, the death of Ustad Zakir Hussain provided an occasion for the reopening of debates among the origins and evolution of the tabla.
- Word ‘tabla’ – It comes from the Arabic word ‘tabl’ which means Drum.
- Origin – While some trace its origin to Persian Naqarra, Hussain traced the origin story of the tabla through the evolution of the styles of dhrupad and khayal.
Dhrupad, a form of Indian Classical music, its origin can be traced back to the chanting of vedic hymns and mantras. It is a form of the Gandharva Veda, the Vedic science of music, which is a branch of Sama Veda.
- The most common disagreement concerns whether or not the tabla originated in pre-Islamic India.

- Evolution – The classical tabla is a relatively recent tradition, most likely beginning sometime in the 1700s.
- It became the main accompaniment instrument for the vocal style known as khyal which helped to raise tabla’s status and popularity.
|
Khayal
|
- It is the most dominant North Indian classical vocal music offers the performer more freedom and a greater scope for improvisation than the older vocal genre ‘Dhrupad’.
- Origin – Khyal emerged during the Mughal period, when Persian music influences blended with local Indian traditions.
- It came into being after the temple traditions of dhrupad & prabandh gayaki were fused with qalbana, the Sufi music (later called qawwali), by the 14th century Sufi saint & musician Amir Khusrau.
|
Amir Khusrau was patronised by Sultan Alauddin Khalji (1296-1316) of Delhi.
- Major developments – It took place during the reign of Emperor Muhammad Shah of Delhi (1719-1748), whose court host the launch of the sitar and maturation of khayal vocalism.
Muhammad Shah was an aesthete, and a great patron of music and the other arts, because of which he was referred to as “Rangeela”, the Colourful.
- Tabla gharanas - they are different from vocal and other instrumental gharanas and rest on 3 broad principles
- The technique.
- The style of composition - Language/ construction/ phraseology of the tabla syllable in various compositions.
- The individual philosophy of the great masters of each school.
- 6 gharanas of tabla – They are known by the places where they evolved.
- Punjab, Purab (also known as the Banaras gharana), Delhi, Ajrara, Lucknow and Farrukhabad.
- Baaj (playing style) –It is more pakhawaj-based for the 1st 2 gharanas.
- Purab’s crisp and clear sounds are very well suited to Kathak.
- Punjab gharana – A mathematical approach, with difficult divisions of beats, is preferred.
- It had offshoots or sub-gharanas such as Talwandi and Naiwala.

Reference
The Indian Express| Evolution of the Tabla and its Various Gharanas
Multi-taxon Global Freshwater Fauna Assessment
Why in News?
The recently published study of multi-taxon global freshwater fauna assessment has identified Western Ghats as a hotspot of threatened freshwater species.
- Study by – IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
- Global assessment – It evaluates the extinction risk and conservation status for diverse freshwater fauna groups.
- It is the 1st ever multi-taxon global freshwater fauna assessment for the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- It is a comprehensive assessments involving contributions from more than 1,000 species experts over 20 years.
- It underscores the historical underappreciation of freshwater ecosystems in global environmental governance
- Coverage – 23,496 Decapod crustaceans, Fishes and Odonates.
- Findings – It revealed that a staggering 1/4th of the freshwater fauna are threatened with extinction, and a record of 89 confirmed and 187 suspected extinctions since 1500 AD.
- Hotspots of Threatened Freshwater Species
- Lake Victoria - Kenya, Tanzania & Uganda.
- Lake Titicaca - Bolivia & Peru.
- Wet Zone - Sri Lanka.
- Western Ghats - India.
- Threat in Western Ghats – It harbours over 300 freshwater fish species of which more than 1/3rd face extinction.
Western Ghats is the only region in Asia with 2 endemic families of freshwater fishes which are exclusively found in groundwater and subterranean systems.
The iconic Humpbacked mahseer, a critically endangered megafish that can grow up to weigh 60 kg, was found in Western ghats.
- Among Indian States, Kerala has the highest number of threatened freshwater fishes, with 74 of its 188 fish species for which Red List assessments are available categorized as threatened.
Periyar River stands out as a critical conservation priority due to its high concentration of endemic and threatened freshwater fish species.
|
Threats
|
Impact on Freshwater Species
(Decapods, Fishes and Odonates)
|
|
Pollution
|
54%
|
|
Dams and water extraction
|
39%
|
|
Land-use
|
37%
|
|
Invasive species and disease
|
28%
|
|
Habitat loss and degradation
|
84%
|
|
Threats
|
Impact on Tetrapods
|
|
Agricultural practices
|
74%
|
|
Logging
|
49%
|
Climate change and severe weather events pose a substantial risk, impacting nearly 1/5th of threatened freshwater species.
Reference
The Hindu| 1st Multi-taxon Global Freshwater Fauna Assessment
EmpowHER Biz (Sapno Ki Udaan)
Why in News?
Recently, the EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan was launched to boost women entrepreneurship in retail.
- Launched by – Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) of NITI Aayog in partnership with New Shop (India’s largest 24/7 convenience retail chain) under its Award to Reward (ATR) program.
New Shop operates a network of over 200 round-the-clock convenience retail stores which are currently present in 35 cities across 18 states. It is committed to empowering over 10,000 entrepreneurs in India by 2030 as it continues to grow its footprint nationwide through a franchising model.
- Launched for – Women from Delhi, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat.
- Aim – To empower women entrepreneurs by equipping them with the skills and resources needed to succeed in the organized retail sector.
- To create a robust retail ecosystem that empowers women entrepreneurs and drives sustainable growth in the sector.
- Role – It will offer mentorship and comprehensive training.
- It will cover retail management, digital tools, financial literacy and business development to aspiring women entrepreneurs.
- It also provides for financial support, or the opportunity to join the New Shop franchising ecosystem
- Selection – 50 participants aged 18–35 selected, will be selected through an online application process based on specific criteria.
- Top 20 participants receive a 100% waiver on New Shop franchise fees.
|
Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP)
|
- It is an aggregator platform.
- Incubated in – 2018, by Niti Aayog.
- Aim – To empower women entrepreneurs by overcoming information asymmetry and providing continuum of support across different pillars
- Access to Finance
- Market Linkages
- Training and Skilling
- Mentoring & Networking
- Compliance & Legal Assistance
- Business Development Services.
- It transitioned into a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) in 2022.
- Partners – Over 30 public and private sector partners.
- Role – It fosters collaboration to develop scalable and impactful programs that benefit women entrepreneurs.
- Since 2023, the ‘Award to Reward’ initiative under WEP offers a plug and play framework for stakeholders to develop impactful programs.
|
Reference
PIB| Launch of EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan
Z-Morh Tunnel
Why in News?
The Z-Morh tunnel is to be inaugurated by the Prime Minister on January 13, 2025 that was started in 2018.
- Z-Morh tunnel – It is named after the Z-shaped stretch of road that the tunnel has replaced (Z-Morh translates to “Z-turn” in English)
- Aim – To provide all-weather connectivity to the Sonamarg tourist town.
- Location - Between Gagangir and Sonamarg in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Construction – It is built under the Mountain glacier of Thajiwas Glacier between Gagangir and Sonamarg.
- Need - At present, the Gagangir-Sonamarg stretch of the road gets blocked by heavy snowfall and avalanches that hit the area every year.
- Features – It is a 6.5 km long 2-lane road tunnel and the main tunnel is 10.8 metres long, with a modified
- Horseshoe shaped tunnel – 7.5 metres.
- D-shaped ventilation tunnel – 8.3 metres.
- Advantage - It takes only 15 minutes to travel the 6.5 km long tunnel compared to hours over the zig-zag road up and down the hills.
- Significance - It is to become the 1st strategic corridor between Kashmir and Ladakh.
- It will also enhance military logistics and boost tourism and the economy.
- It will help the employment of local youth and boost tourism and allied activities in the area.
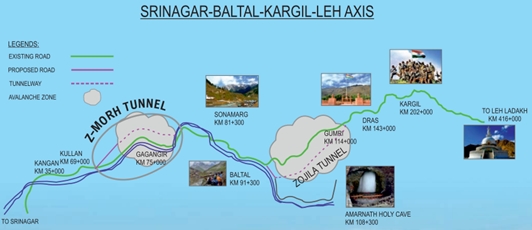
Z-Morh Tunnel together with the adjacent Zoji-La Tunnel, on the Srinagar-Leh Highway will provide year-round weather-proof connectivity to Baltal (Amarnath cave), Kargil and other places in the Ladakh region.
Zojila Tunnel, which is under construction will be the longest tunnel in Asia, which cut through the Himalayan range at Zojila Pass to reach the Kargil district in Ladakh.
Reference
The Hindu| Z-Morh Tunnel for Winter Tourism
|
One Liners 10-01-2025
|
|
Schemes and programmes of Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare
|
|
Agriculture production
- Food grain production – For 2023-24 is recorded at 332.30 million tonnes.
- Horticultural production – Stands at 352.23 million tonnes, according to the third advance estimates.
Minimum Support Price
- Government has increased the MSP for all mandated Kharif, Rabi and other commercial crops.
- Fixing of MSP at one-and-a half times the cost of production.
Institutional credit for agriculture sector
- The ground-level credit disbursement in agriculture has experienced a significant increase of 349%, including both short-term and long-term credit.
- Kisan Credit Card scheme – Short-term credit investment through the Kisan Credit Card scheme has grown 270%.
National Beekeeping & Honey Mission (NBHM)
- Launched – Under the AatmaNirbhar Bharat initiative, aims to promote scientific beekeeping and achieve the ‘Sweet Revolution.
- It focuses to establish infrastructure like Integrated Beekeeping Development Centres (IBDCs), Honey Testing Labs, Beekeeping Equipment Manufacturing Units and Custom Hiring Centres.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)
- A Centrally Sponsored Scheme for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector covering fruits, vegetables, root & tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa and bamboo.
- Under MIDH, Union Government contributes 60%, of total outlay for developmental programmes in all the states except states in North East and Himalayas, 40% share is contributed by State Governments.
- In the case of North Eastern States and Himalayan States, the Union Government contributes 90%.
National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds)
- It aims to boost domestic oilseed production and achieve self-reliance in edible oils. With a financial outlay of Rs 10,103 crore, it will run from 2024-25 to 2030-31.
Sub-Mission On Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM) Scheme
- Launched – In 2014-15.
- Objective – Provides financial assistance for purchasing agricultural machinery and establishing Custom Hiring Centres (CHCs), High-Tech Hubs, and Farm Machinery Banks.
Crop Residue Management (CRM) Scheme
- Launched in 2018-19, supports Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Delhi in addressing air pollution and subsidizing machinery for crop residue management.
Extension Reforms (ATMA) Scheme
- ATMA, a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, presently is being implemented in 739 districts of 28 states & 5 UTs in the country.
- The scheme promotes decentralized and farmer-friendly extension system in the country.
- Objectives – To support State Government’s efforts and to make available latest agricultural technologies and good agricultural practices in different thematic areas of agriculture and allied areas to farmers through different extension activities.
Climate resilient Varieties
- Climate resilient crop varieties of cereals, oilseeds, pulses, forage crops, fibre crops and sugar crops have been developed specially for extreme climate including.
- ICAR has recently released 109 climate resilient varieties which will help the farmers for its adoption based on agro climatic conditions.
|


