DART Mission for Didymos & Dimorphos
A new study found that rocky debris blasted away from a football stadium-sized asteroid, Dimorphos, during the DART mission could create the 1st human-made meteor shower known as the Dimorphids.
- Discovery - Didymos which means "twin" in Greek was discovered on April 11, 1996, by researcher Joseph Montani of Spacewatch at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Tucson, Arizona.
- Asteroid Didymos and its small moonlet Dimorphos make up a binary asteroid system.
- The small moon (Dimorphos) orbits the larger body (Didymos).
- They were chosen for DART mission as they pass relatively close to Earth.
- It found that the DART mission's kinetic impactor technique could effectively change an asteroid's trajectory.
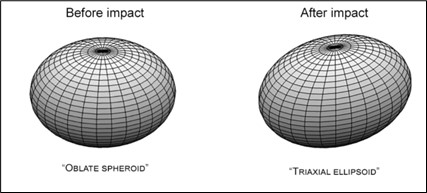
- After launching of the mission it shows the impact changed not only the motion of the asteroid, but also its shape.
- The entire shape of the asteroid has changed, from a relatively symmetrical object to a ‘triaxial ellipsoid’ – something more like an oblong watermelon.
DART Mission
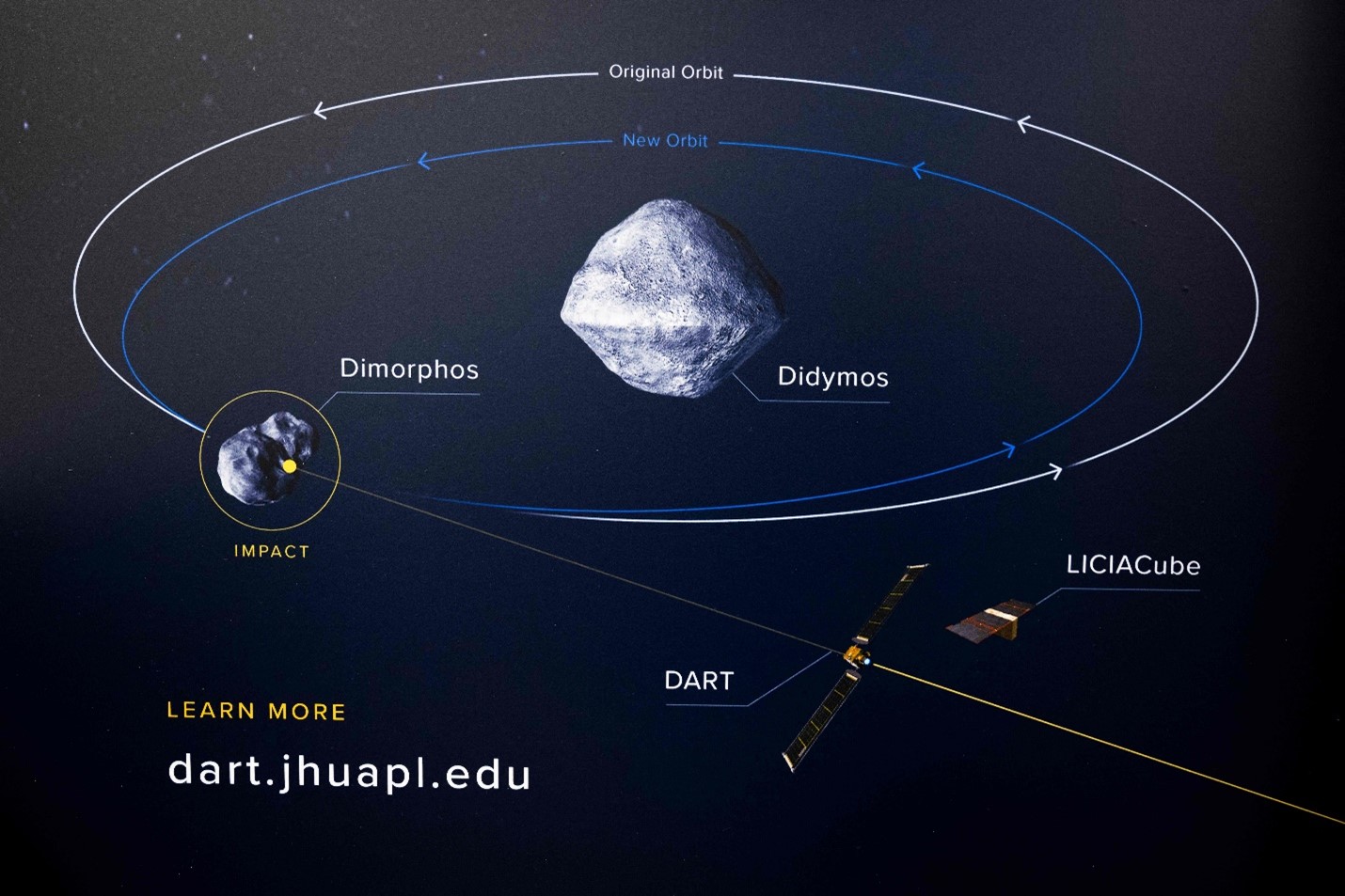
- DART - Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART).
- Launched by – NASA in 2021.
- Aim - To test the newly developed technology that would allow a spacecraft to crash into an asteroid and change its course.
- Targets - Asteroid Didymos and its moonlet Dimorphos.
- It is a part of the NASA’s larger platenary defence Strategy.
- Methodology - It is the 1st Kinetic Impactor Method of planetary defence, where a DART spacecraft will be colliding with the asteroid Dimorphos.
- The Kinetic Impactor Method involves sending one or more large, high-speed spacecraft into the path of an approaching near-earth object.
- This could deflect the asteroid into a different trajectory, steering it away from the Earth's orbital path.
- Propellant - It has 2 solar arrays and uses hydrazine propellant for manoeuvring the spacecraft.
- Thruster - It also carries about 10 kg of xenon which will be used to demonstrate the new thrusters called NASA Evolutionary Xenon Thruster–Commercial (NEXT-C) in space.
- NEXT-C gridded ion thruster system provides a combination of performance and spacecraft integration capabilities that make it uniquely suited for deep space robotic missions.
- It's a type of electric propulsion that uses electricity to accelerate xenon propellant to speeds of up to 90,000 miles per hour.
- Imager - The spacecraft carries a high-resolution imager called Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical Navigation (DRACO).
- Images from DRACO will be sent to Earth in real-time and will help study the impact site and surface of Dimorphos.
Reference
Live mint | DART mission created ’1st human-made’ meteor shower
Curcuma ungmensis
A newly identified species of 'Curcuma,' named Curcuma ungmensis, was recently discovered by researchers in Ungma Village, located in Mokokchung district of Nagaland.
- Genus – Curcuma.
- Family- Zingiberaceae.
- Curcuma is among the largest and most significant genera within this family, with well-known members like turmeric (Curcuma longa), black turmeric (Curcuma caesia), and mango ginger (Curcuma amada).
- Nomenclature - Curcuma ungmensis is named after Ungma village, where it was found.
- Size - It reaches heights of 65-90 cm.
- Appearance – It features striking yellow flowers at maturity, flowering occurs during the rainy season.
- Habitat - The plant thrives in warm, tropical climates.
- Distribution - Curcuma is extensively found throughout South and Southeast Asia, as well as in southern China. Some species can also be located in northern Australia and the South Pacific.
- In India, approximately 40 species of this genus are present, predominantly in the northeastern and southern states, along with the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Uses - This species is a rhizomatous herb with underground stems (subterranean stem).
- The vibrant inflorescence makes it a promising candidate for use as a cut flower.
- Once domesticated, it has potential as an ornamental ground cover in gardens.

Reference
The Hindu | New species of genus Curcuma in Nagaland
Kawasaki disease
A Pediatric study recently revealed that Kawasaki disease cases among children have increased in India after COVID-19 pandemic.
- Kawasaki is a rare disease that causes inflammation of the blood vessels and a high fever that lasts for more than 5 days.
- Kawasaki Disease (KD) is sometimes called mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome.
- Kawasaki disease most often affects the heart arteries in children. Those arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart.
- It is one of the most common form of acquired heart disease in children.
- Cause - The cause of Kawasaki disease is unknown, but it may be due to an immune system reaction to a virus or a genetic link.
- Symptoms - A high fever, red eyes, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, a red rash on the middle of the body, a red tongue, and swollen hands and feet.
- Vulnerable Age group - Kawasaki disease happens most often in children 6 months to 5 years of age.
- Contagiousness - Kawasaki disease is not contagious and cannot be spread from one person to another
- Complications - Cardiovascular complications include aneurysm formation, heart failure, myocardial infarction, and valvulitis.
- Prevention - There is no way to prevent Kawasaki disease. But Kawasaki disease is often treatable.
- Treatment - With early treatment, most children get better and have no long-lasting problems.
- Affected countries - It occurrs in an estimated 10 to 20 out of 100,000 children younger than age 5 in the United States and Canada.
- In Japan, Korea and Taiwan, it affects 50 to 250 out of 100,000 children younger than 5.
Recent findings
Multisystem inflammatory disease in children (MIS-C) vs Kawasaki Disease
- A recent study revealed that hyperinflammatory shock with clinical features similar to those of Kawasaki disease (KD) after COVID-19 infection in 2020.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) and U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have named this new syndrome a multisystem inflammatory disease in children (MIS-C).
- According to the study, the clinical manifestations of MIS-C overlap with those of KD, including fever, skin rashes, conjunctivitis, and mucocutaneous manifestations.
- However, MIS-C is more commonly associated with left ventricular dysfunction (30%–40%) and shock, gastrointestinal abnormalities, and neurological manifestations than KD.
- It also revealed that KD following SARS-CoV-2 infection has clinically different characteristics from conventional KD.
References
- Financial Express | Kawasaki disease
- Cleveland Clinic | About Kawasaki Disease
New Study on butterfly species
A recent study published in the Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society highlights conservation gaps and calls for reassessing conservation status of several species.
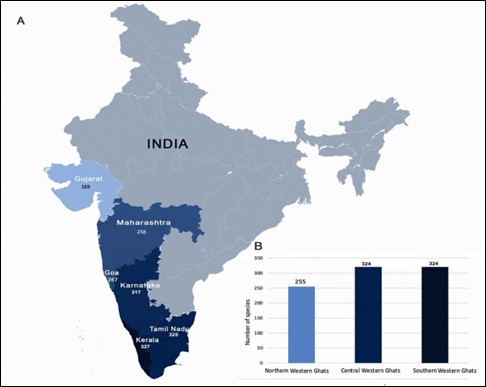
- It highlights that the diversity of butterfly species is highest in the southern Western Ghats and gradually diminishes northward.
- Distribution
|
Region
|
Species
|
|
Western Ghats
|
337 butterfly species.
|
|
Kerala
|
328 (highest number)
|
|
Tamil Nadu
|
326
|
|
Karnataka
|
317
|
- Diversity- The southern and central Western Ghats each have 324 species, while the northern Western Ghats have only 255 species.
- Butterfly families- The species belong to 6 families:
- Papilionidae (19)
- Pieridae (34)
- Nymphalidae (100)
- Riodinidae (2)
- Lycaenidae (99)
- Hesperiidae (83)
- Endemic- There are 40 strictly endemic species in the Western Ghats.
- Listed Threatened Species
- IUCN Red List- Less than 7% (22 species).
- Wildlife (Protection) Act- 71 species (21%) are protected under this act with amendments up to 2022.
- Near threatened- 2 species and rest as 'least concern'.
- Common species like crimson rose, Indian common rose, and Indian tiny grass blue could be excluded from the IUCN Red List.
- Concerns
- Some strictly endemic and rare species are not protected under WLPA; and
- While certain common species are listed on the IUCN Red List, some truly threatened and rare species are not included.
- Suggested species for WLPA inclusion- Sahyadri green yellow, Nilgiri clouded yellow, red-eye bushbrown, Palni bushbrown, Nilgiri fritillary, and cloud-forest silverline.
- Rare species for IUCN Red List re-evaluation- Abnormal silverline, yellow-base flitter, Malabar banded swallowtail, and Travancore evening brown.
Reference
The Hindu | Study on butterfly species
Carrhotus piperus
A new species of jumping spider, Carrhotus piperus, has been identified in the lower Palani Hills of Tamil Nadu.
- Carrhotus piperus – It is a new species of jumping spider of genus Carrhotus Thorel.
- Sex – It is male carrhotus species.
- Habitat - Pepper (Piper nigrum) plants.
- Piperus – It is the specific epithet that describes the spider’s distinctive pepper plant (Piper nigrum) habitat.
- Unique feature - Unique prolateral protrusion and beak-shaped embolus distinguish it from its closely-related species.

|
Carrhotus Thorell
|
- It is a jumping spider genus that was described by Thorell in 1891.
- It encompasses 36 currently valid species and with 9 known from India.
- Number of Species – With the new discovery , the number of Carrhotus species in India increased to 10, and to 37 globally.
- Distribution - Asia, Europe, Africa, and Brazil
- Description - 16 described based on both sexes, 11 on males alone, and 9 on females alone.
- In India, no Carrhotus species are known solely from females.
- There are several species from Nepal, Bhutan, and Sri Lanka known only from female specimens.
|
|
Jumping Spiders
|
- Jumping spiders are a group of spiders that constitute the family Salticidae.
- It the largest family of spiders with 13% of all species.
- As of 2019, this family contained over 600 described genera and over 6,000 described species.
- They leap great distances to move and stalk prey.
- Unlike other jumping insects that rely on large, muscular back legs, jumping spiders have a hydraulic system that propels them forward.
|
References
- The Hindu | Carrhotus piperus
- JIBS | Carrhotus Thorell, 1891




