Teal Carbon
Recently , India’s first study on ‘teal carbon’ was undertaken at Keoladeo National Park (KNP) in Rajasthan.
- Teal Carbon – It is the organic carbon stored in non-tidal freshwater wetlands.
- It is colour-based terminology that reflects the classification of the organic carbon based on its functions and location rather than its physical properties.
- Components - It encompasses carbon sequestered in vegetation, microbial biomass, and dissolved and particulate organic matter.
- Sources - Peatlands, freshwater swamps, and natural freshwater marshes account for significant amount of this storage.
- Global level storage - Across the ecosystems, 500.21 petagrams of teal carbon (PgC) is strored.
Petagrams of carbon (PgC) is a unit to measure carbon and it is equivalent to 1015 grams.
- Climate Mitigation Tool - It can be used as a tool to mitigate climate change caused by anthropogenic pollution in the wetlands.
- Benefits of teal carbon ecosystem –Increase in the ground water level, flood mitigation and heat island reduction, supporting a sustainable urban adaptation.
- Regulating GHG - Equivalent to coastal wetlands, they have the capacity to regulate greenhouse gases.
- Other Carbon Forms
- Black and Brown carbons - They are primarily produced by incomplete combustion of organic matter from sources such as wild fires, fossil fuel combustion, and industrial activities.
- Blue carbon - It is the carbon stored in coastal and marine ecosystems.
- Coastal wetlands, including seagrass meadows, mangroves and tidal marshes, are major blue carbon ecosystems and are often termed “blue forests”.
References
The Hindu | India’s first ‘teal carbon’ study
PresVu
Recently, a Mumbai-based company has developed a new eye drop to reduce dependency on reading glasses for individuals affected by presbyopia.
- PresVu – It is a first of its kind eyedrop in India to treat presbyopia.
- Developed by - Entod, Mumbai-based pharmaceuticals company.
- Active Ingredient – PresVu contains 1.25% concentration of Pilocarpine.
In India, the government decides on the ceiling price of pilocarpine in 4% and 2% concentrations.
- Working - The compound contracts the iris muscles, which control the size of the pupil, to focus better on nearby objects.
- It uses advanced dynamic buffer technology essentially, a base solution, to adapt to the pH level of tears.
- This ensures that the eye drop has consistent efficacy and safety for extended use.
- Side effects - PresVu is a prescription-only medicine and its impact is unlikely to last beyond four to six hours.
- Regular use of PresVu may lead to itching and redness, eyebrow pain, and muscle spasms in the eyes.
|
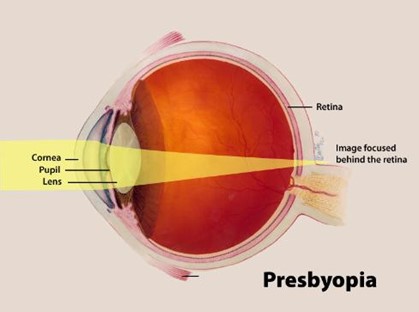
Presbyopia
|
- It is an age-related farsightedness condition in which the eyes gradually lose the ability to focus on nearby objects.
- People usually start to develop presbyopia at around the age of 40.
- Symptoms - Blurry close-up vision, headaches, and eye strain.
- No Cure - There's no cure for presbyopia, but there are several treatments, including corrective lenses, contact lenses, and surgery.
|
Reference
Indian Express | PresVu
Sakthan Thampuran
Recently, Minister of State for Tourism pledged to renew the statue of Sakthan Thampuran.
- Sakthan Thampuran - Raja Rama Varma Kunjipillai or Rama Varma IX, is called as Sakthan Thampuran.
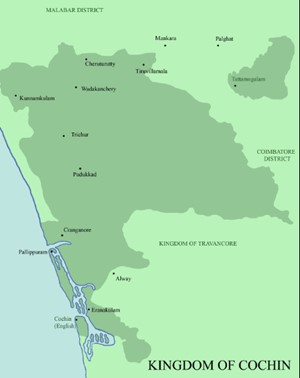
- Kingdom – Cochin
- Ruling Period - 1790 to 1805.
- Birth – 1751
- Parents - Ambika Thampuran and Chendose Aniyan Namboodiri of the Cochin royal family.
- Sakthan – He was raised by an aunt who called him Sakthan, meaning ‘powerful’.
- Cochin kingdom - It was part of the Late Chera Empire, covered the regions between Ponnani in Malappuram and Thottappally in Alappuzha.
- Heir apparent - Sakthan Thampuran became heir apparent in 1769 as an 18-year-old.
- Strategist - He advised his king to maintain friendly relations with both the Dutch and the English.
- Travancore Invasion - Sakthan is said to have orchestrated Mysore’s attempt to invade the Travancore kingdom.
- Powney treaty - This would result in the Powney treaty which freed the Cochin kingdom from its allegiance to Mysore, and helped formalise its relations with the British.
- Ending Yogiatirippads - He ended the institution of the Yogiatirippads — the erstwhile spiritual heads of the Vadakkumnathan and Perumanam temples.
- He entrusted temple management to the government from Yogiatirippads.
- Capital Transfer – He transferred the seat of the Cochin kingdom from Thrippunithura to modern-day Thrissur.
- Trade Encouragement - The king encouraged merchants of all religions and British officials to relocate to the city.
- Revenue Management - He also overhauled and firmed up the kingdom’s finances, personally overseeing revenue management.
- Thrissur Pooram – He started the Thrissur Pooram in 1797 as an alternative to the Arattupuzha Pooram.
- The Thrissur Pooram was conceived as an opportunity for the major temples in Thrissur to come to pay their respects to Lord Shiva, the presiding deity at the Vadakkumnathan Temple.
Reference
Indian Express | Sakthan Thampuran
Global guidance on antibiotics pollution from manufacturing
Recently WHO released first ever global guidance to tackle antibiotic pollution from manufacturing processes.
- Guideline – Guidance on wastewater and solid waste management for manufacturing of antibiotics.
- Released by - World Health Organization (WHO)
- Aim - Foster a collective effort to mitigate the environmental impact of antibiotic manufacturing.
- Framework – It offers a scientific framework for regulators, industry players and other stakeholders to implement effective controls against antibiotic pollution.
- Comprehensive Approach - It covers all steps from the manufacturing of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and formulation into finished products, including primary packaging.
- Antibiotic pollution control standards – It provides scientific basis for regulators, procurers, inspectors and industries to include robust antibiotic pollution control in their standards.
- 3 Core elements – It outlines three core elements and the parties responsible for implementing each one.
- Targets - Defining targets for resistance selection and ecological effects, based on exposure and risk assessments.
- Risk Management - Establishing risk management processes to achieve these targets
- It is done by tools such as hazard analysis and critical control points, alongside internal audits and public communications.
- Audits - Conducting independent audits to verify that targets are being met.
- Guiding Principles
- Precautionary approach for target setting
- Progressive improvement towards meeting these targets.
|
Anti-Microbial Resistance (AMR)
|
- AMR occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites no longer respond to medicines.
- It makes people sicker and increasing the risk of spread of infections that are difficult to treat, illness and deaths.
- Causative factors - AMR is driven largely by the misuse and overuse of antimicrobials.
- The emergence and spread of AMR caused by antibiotic pollution could undermine the effectiveness of antibiotics globally.
- Antibiotic Pollution - Pharmaceutical waste from antibiotic manufacturing can facilitate the emergence of new drug-resistant bacteria.
- It includes the medicines produced at the manufacturing sites and the unscientific disposal of them as waste after use.
- High levels of antibiotics in water bodies downstream of manufacturing sites have been widely documented.
- Currently, antibiotic pollution from manufacturing is largely unregulated and quality assurance criteria typically do not address environmental emissions.
|
Reference
DownToEarth | WHO global guidance on antibiotic pollution
Operation Bhediya
Recently 5th wolves were trapped in Bahraich after deadly attacks.
- Operation Bhediya – It is the effort of Uttar Pradesh department forest department to capture wild wolves in the Bahraich region.
- It has been carried out in about 35 villages in Bahraich District under threat of wolf attacks.
- Launched by – Forest Department of Bahraich District, Uttar Predesh.
- Measures Taken - The operation includes increased monitoring of known wolf habitats and areas with frequent attacks to track their movements and prevent further incidents.
- Wildlife management - Improve overall wildlife management practices, including better waste management.
- Prevention - Creation of barriers to prevent wolves from entering human settlements.
- Thermal drones – They are being deployed to track the wolf's movements.
- Camera Traps - They were installed to automatically trigger by motion in its vicinity by the presence of the animal.
- Pugmarks - Identifying pugmarks and gathering intelligence from residents.
- Tranquilise - Permission to tranquilise the animals has also been granted by the Chief Wildlife Warden.
- Wildlife Disaster area - Uttar Pradesh government has declared the Bahraich district as a 'Wildlife Disaster' affected area.
- It will expedite the ongoing 'Operation Bhediya' to catch the animals involved in the attack on humans and help the affected families to get an ex-gratia amount without much trouble.
To Know more about the wolves , Click Here
Reference
Hindustan Times | Operation Bhediya
