7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Forest Fires in India
Burn Indices
Zinc Gluconate
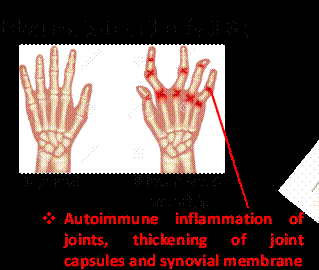
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reservations for Divyangjan
Constitutional provisions on reservations

NATGRID
National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB)
Himalayan Viagra
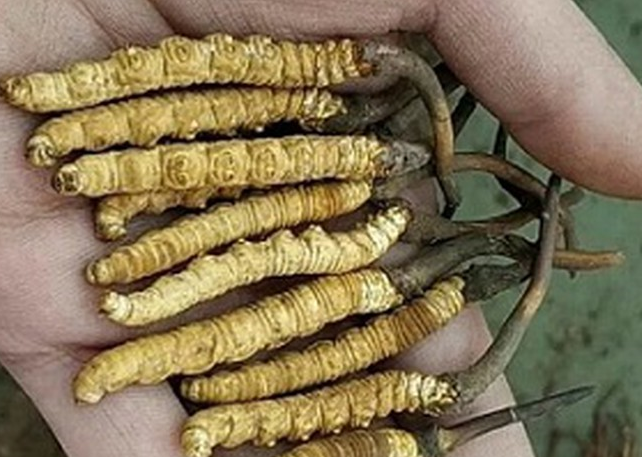

Source: PIB, the Hindu