The Union government recently launched the ‘Amrit Gyan Kosh’ Portal & Faculty Development portal.
Amrit Gyan Kosh Portal
Mission Karmayogi is an initiative aimed at transforming civil servants from 'Karmachari' (employee) to 'Karmayogi' (dedicated worker) through competency-driven capacity building.
Faculty Development Portal
|
National Capacity Building Commission (NCBC) |
|
Reference
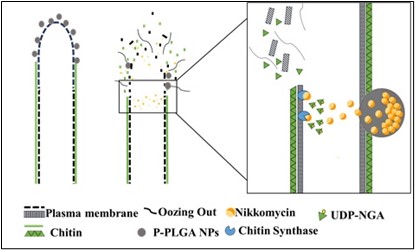
Researchers have developed a porous composite xerogel dressing that provides a crucial solution for uncontrolled haemorrhage.
Uncontrolled haemorrhage, accounts for over 40% of trauma-related deaths, is often inadequately managed by traditional methods.
Reference
PIB | Porous composite xerogel
Recently, India and Maldives renewed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to train 1,000 Maldivian civil service officers from 2024 to 2029.
References
The Education Ministry recently released the Indian Ranking Report for 2024.
Key Highlights of the report
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)

References
Recently, the Government of India has issued Operational Guidelines for the Implementation of 'Model Solar Village’ under PM-Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana.
References