7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
NASA New Missions
Yara Virus
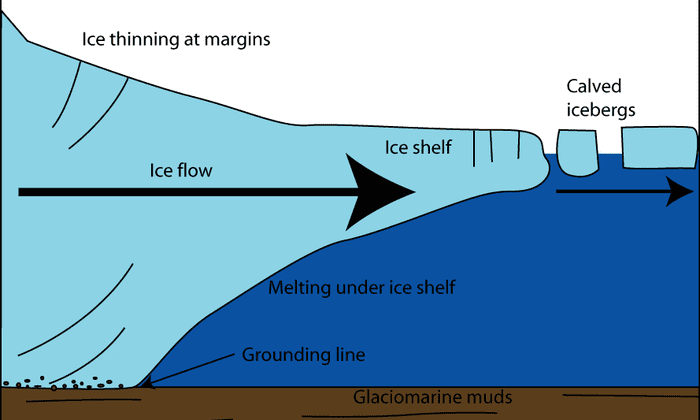
Thwaites Glacier
Indian Scientific Expedition to the Southern Ocean 2020
India’s Polar Stations
Wainganga
Godavari River
Source: PIB, Indian Express, the Hindu