7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Quinine Nongladew

Gharials
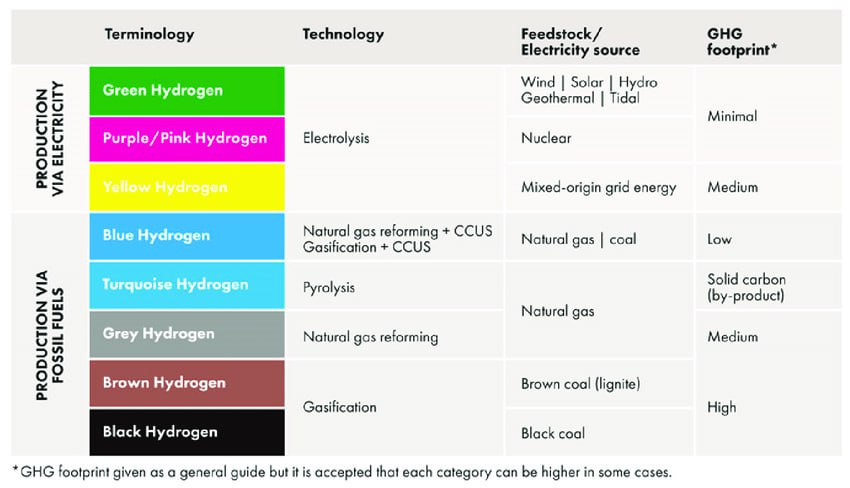
Three important Crocodilias in India
Chambal River
Ghaghara River
SAMARTH ERP
National Mission on Education through Information and Communication Technology
Technical Education Quality Improvement Programme
Asian Infrastructure Investment Banks
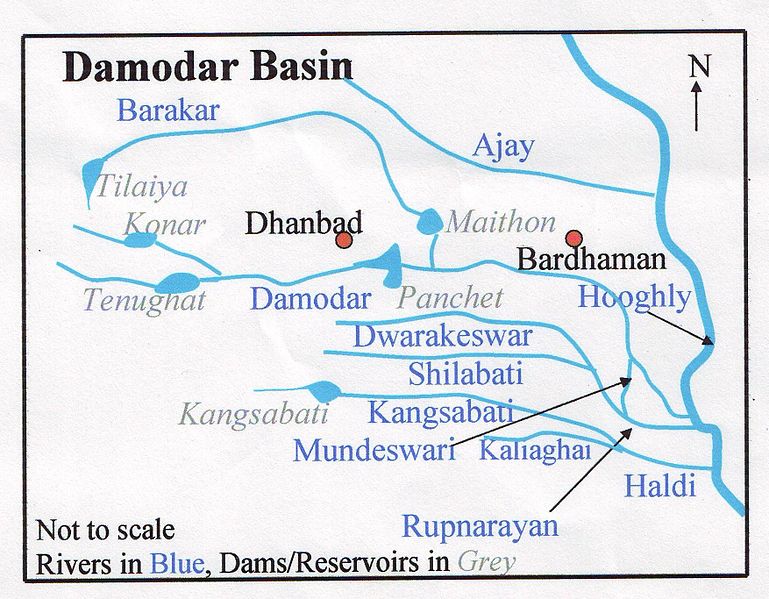
Damodar River
Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020
Food and Agriculture Organization
Source: The Hindu. Down To Earth, News on Air