The UPSC recently issued advertisement to recruit 45 candidates through lateral got criticism from opposition party that the centre was trying to bypass reservation policies.
Joint Secretary is the third-highest rank (after Secretary and Additional Secretary) in a Department, and functions as the administrative head of a wing in the Department.
References
8 persons were recently injured after 2 factions of the Namdhari sect opened fire at each other over a land dispute near the dera in Sirsa’s Jiwan Nagar in Haryana.
References
Scientists recently found that prokaryotes are remarkably resilient to climate change and as a result, could increasingly dominate marine environments.
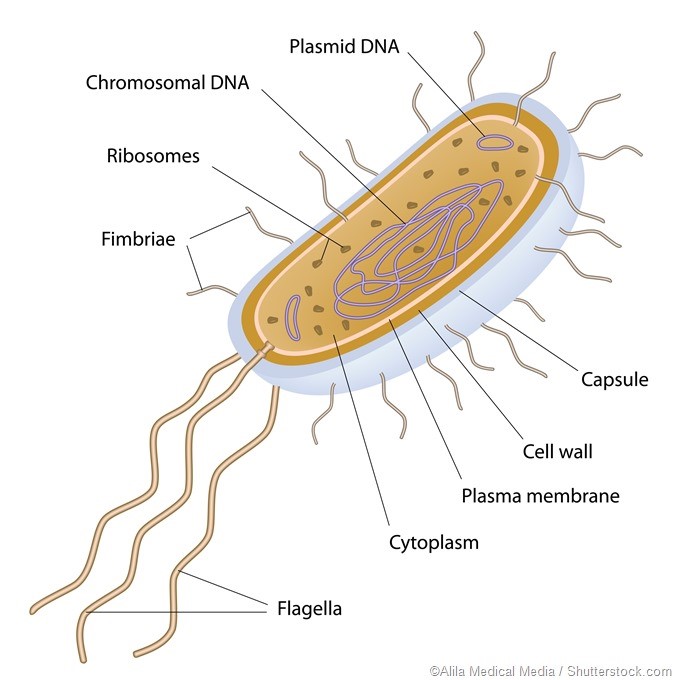
References
According to a recent study, Climate change may decrease the distribution range of the Malabar Tree Toad (MTT) by up to 68.7 %t of the current estimated distribution in India’s protected areas (PAs).
Toad is a common name for certain frogs, especially of the family Bufonidae, that are characterized by dry, leathery skin, short legs, and large bumps.
|
Habitats of Malabar Tree Toad |
|
|
Tamilnadu |
|
|
Kerala |
|
|
Karnataka |
|
|
Goa |
|

Amphibians are one of the most sensitive groups to the impacts of climate change due to their unique ecology.
References
The Indian student team has bagged multiple prestigious medals at the 17th edition of the International Earth Sciences Olympiad (IESO).
References