7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
COVID and Destruction of Forests
IBM’s Summit and COVID-19
Saranda and Chaibasa Iron Ore Reserves
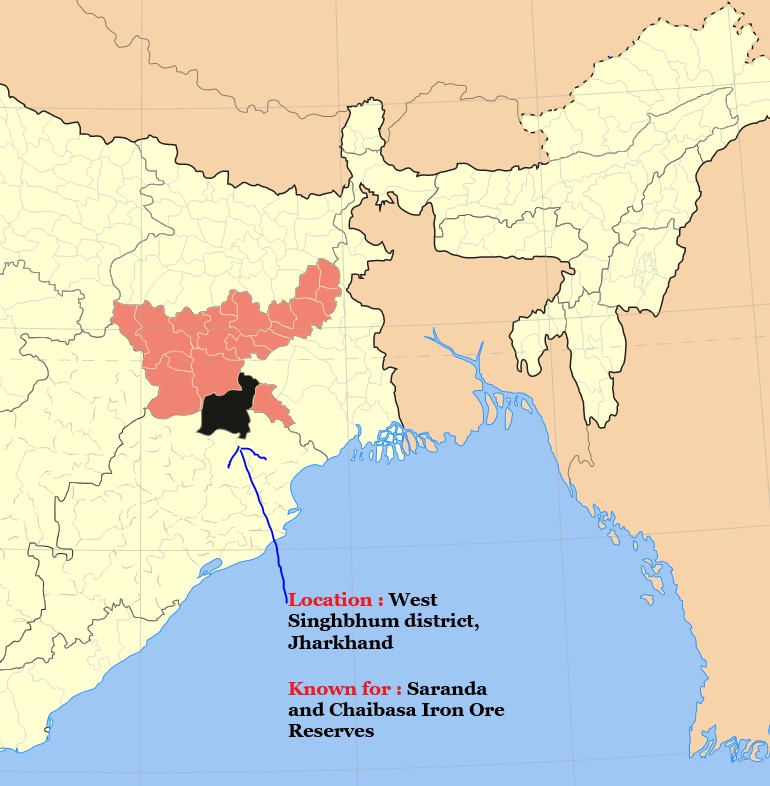
Management Plan for Sustainable Mining (MPSM)
Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education
Enzyme SPRK1
Bengaluru’s Water Conservation Score
JSA Water score card
Solar Eclipse
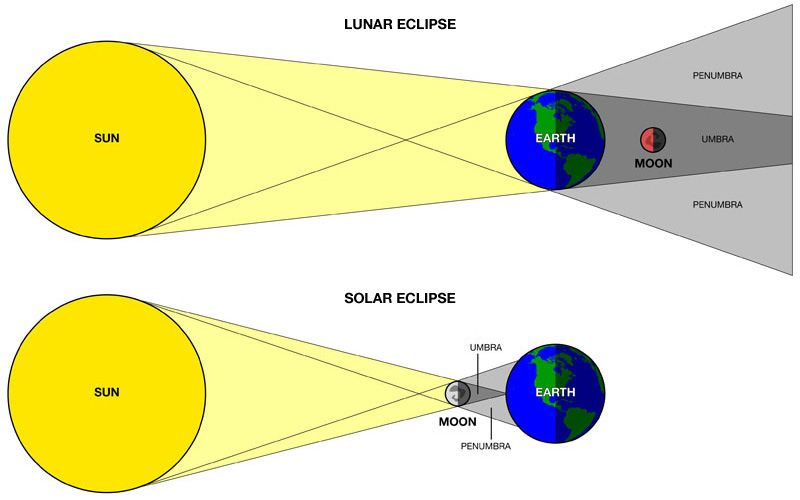
Lunar Eclipse
Umbra, Penumbra and Antumbra
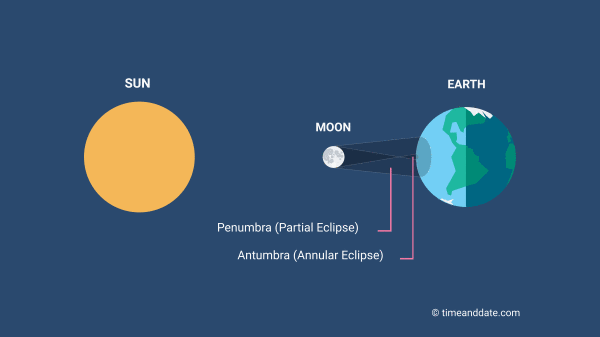
Source: Down to Earth, Indian Express