7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
PM- Matsya Sampada Yojana
PM- Vaya Vandana Yojana
Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises
Rahiv Gandhi Kisan Nyay Yojana
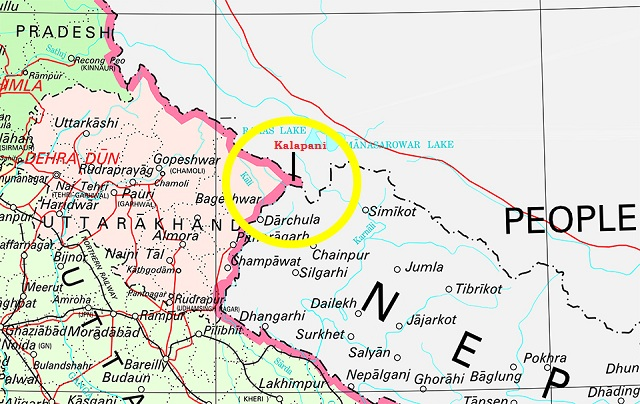
Kalapani Territory
Susta Region
Kali River
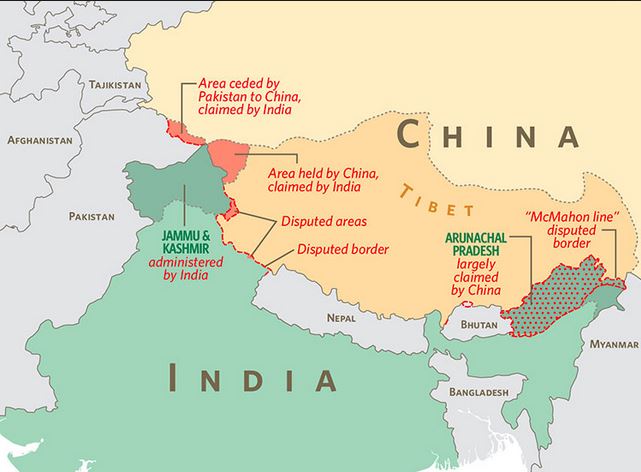
Line of Actual Control
Alzheimer’s Disease
Preventive measures for Alzheimer
Source: PIB, The Hindu, Times of India