7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Positive Pay Mechanism
Trifood
SalivaDirect
Project Dolphin; Project Lion
Gangetic River Dolphin
Asiatic Lion
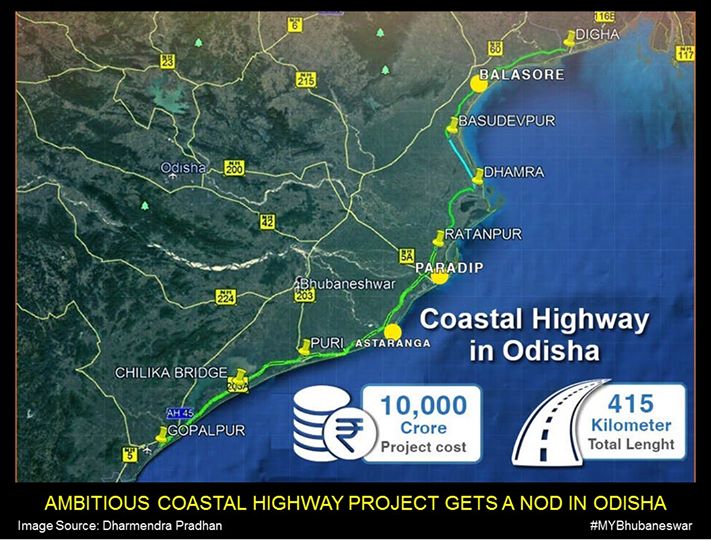
Digha-Gopalpur Coastal Highway
Prakash Purab Utsav
National Recruitment Agency (NRA)
Source: PIB, the Hindu, Times of India, AIR