National Innovation Challenge for Drone Research (NIDAR)
Why in news?
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and Drone Federation India has recently launched NIDAR to boost Talent, R&D and Skill Development in Drone Ecosystem.
- Aim – NIDAR is India’s largest national drone innovation initiative that motivates students and researchers from academia to build collaborative autonomous drones across 2 critical domains:
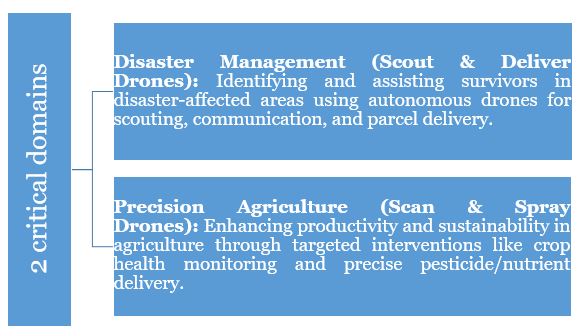
- Launched under – The SwaYaan Initiative.
- Benefits – It offers a total prize pool of INR 40 Lakhs along with opportunities for startup incubation, cloud credits, software support, and internships with India’s leading drone companies.

|
SwaYaan Initiative
|
- SwaYaan is a National Initiative to develop and strengthen India’s UAS/Drone ecosystem, aligning with the Government’s vision to make India a global drone hub by 2030.
- Aim – The program empowers learners from undergraduates to faculty and open learners across five key technical areas through 1,500+ academic, research, and knowledge-sharing activities.
- Ministry – Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Implementation – Through a network of 30 Premier Academic and R&D institutions, including IIT, IISc, IIIT, NITs, IIITDM, C-DAC, and NIELIT Centres.
|
|
Drone Federation India (DFI)
|
- A non-government, non-profit, industry-led body representing 550+ drone companies and 5500+ drone pilots across the country.
- Vision – To make India a global drone hub by 2030, and it promotes the design, development, manufacturing, adoption and export of Indian drone and counter-drone technology worldwide.
- Significance – A premier industry will support participating students in NIDAR by providing mentorship and industry exposure.
- DFI enables ease of doing business, promotes the adoption of drone technology, and hosts several programs like Bharat Drone Mahotsav.
|
References
- PIB | NIDAR
- Swayaan website | Swayaan
- Nidar website | NIDAR
New IT Rules for Removal of Harmful Online Content
Why is in News?
The government is strengthening laws to fight cybercrimes, especially obscene and child abuse content, ensuring better online safety.
Key Provisions for Digital Content Regulation
IT Act, 2000
- Punishes publishing/transmitting obscene or sexually explicit material online.
- Stricter penalties for content involving children in sexually explicit acts.
IT Rules, 2021 (Intermediary Guidelines & Digital Media Ethics Code)
- Intermediaries (including social media platforms) must follow due diligence, or they lose legal protection from third-party content.
- Messaging platforms must identify the first originator of content in cases related to rape, sexually explicit material, or child sexual abuse material (CSAM).
- Intermediaries must remove explicit content within 24 hours if it exposes private areas, nudity, or sexual acts.
- Grievance Appellate Committees established to hear user appeals against social media decisions.
Film & OTT Content Regulation
- CBFC (Central Board of Film Certification) regulates film content under the Cinematograph Act, 1952 and Cinematograph (Certification) Rules 1983.
- Films unsuitable for minors are certified for adult audiences only.
- OTT Platforms must follow a code of ethics under IT Rules, 2021:
- Classify content into age-appropriate categories.
- Restrict access for children to inappropriate content.
- Implement age verification for adult content.
Government Measures to Strengthen Cybercrime Prevention
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal - Allows citizens to report all types of cybercrimes, with a special focus on crimes against children.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) - Established to handle cybercrimes in a coordinated manner.
- Financial assistance provided to States/UTs under the Cyber Crime Prevention against Women and Children Scheme for:
- Setting up cyber forensic-cum-training labs.
- Training law enforcement personnel, public prosecutors, and judicial officers.
- Websites containing child sexual abuse material (CSAM) blocked based on Interpol lists received through the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs) directed to implement the Internet Watch Foundation (UK) & Project Arachnid (Canada) lists to block CSAM websites dynamically.
- Department of Telecommunications (DoT) instructed ISPs to
- Spread awareness on parental control filters.
- Block certain websites containing CSAM.
- Cybercrime awareness initiatives by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA)
- Twitter handle (@cyberDost) for spreading awareness.
- Radio campaigns.
- Handbook for Adolescents/Students on cyber safety.
- MoU signed between National Crime Records Bureau (India) & National Center for Missing & Exploited Children (USA) to share Tipline reports on child sexual exploitation and explicit online content with States/UTs for further action.
Reference
PIB - Government of India Taking Measures against Online Pornography
Centre Government Guidelines
Why in News?
A Bill for regulating coaching centres was tabled in the Rajasthan Legislative Assembly recently.
- New coaching centre bill of Rajasthan - Aim – It would curb the commercialization of coaching institutes and ensure that they operate within a framework prioritizing the well-being and success of students.
- It seeks to mandate minimum quality standards, the registration of coaching centres, and psychological counselling for students.
|
Central government’s January 2024 guidelines
|
Rajasthan Bill’s Key provisions
|
- Only students who are 16 years of age or have completed secondary school examinations can be enrolled in coaching centres.
|
- It has no mention of the age criteria.
|
- It mandated biometric attendance through face recognition technology.
|
- The Bill has no such provision for attendance.
|
- Coaching centres shall abide by the orders issued by the state government regarding national holidays, local holidays as declared by the District Collector and festivals.
|
- Centres should try to customize leaves to coincide with festivals, it omits mention of national and local holidays.
|
- Coaching centres shall not discriminate against any applicant/ student on the basis of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth, descent etc. during the admission and teaching process.
|
- No mention of such provision.
|
- Centres may also make special provisions to encourage greater representation of students from vulnerable communities, including female students and differently abled students.
- The centre’s building and surrounding premises should comply with the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
|
- No mention of such provision.
|
- It regulated the coaching centres by proposing
- A penalty of Rs.25,000 for the first violation of provisions and
- Rs.1 lakh for a second violation, followed by cancellation of registration for subsequent violation(s).
|
- It sets the first fine at Rs.2 lakh and Rs.5 lakh for the second offence, followed by cancellation of the centre’s registration.
|
Reference
The Indian Express - Rajasthan’s new coaching centre bill
Dog-faced Water Snake (Cerberus Rynchops)
Why in News?
Herpetologists recently sighted the dog-faced water snake for the first time in the floodplains at Garemara in western Assam’s Nalbari district.
- It is a rear-fanged, mildly venomous, and semi-aquatic snake.
- It is also known as the South Asian bockadam.
- Appearance – Mottled grey and black colour.
- It is well adapted to brackish water, due to their aquatic habitat they have nostrils placed higher upon their snout giving them a dog-like appearance.
- They have salt glands below upper lip that discard excess salt acquired from the brackish water they consume.
- Size – Grow up to one metre.
- Diet – It is known to hunt for fish and crustaceans in shallow waters, using a sit-and-wait predatory strategy.
- Habitat – Predominantly associated with coastal ecosystems, inhabiting mangroves, coastal mudflats, and estuarine habitats, Inland records of the species are rare.
- Distribution - Across South, Southeast Asia, and parts of Australia002E
- Indian coastal regions in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Kerala, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Breeding – Viviparous – Give birth to young ones.
- Conservation Status
- Threats
- Loss of Mangrove Habitats
- Entanglement in fishing nets.
References
- The Hindu - Dog-faced snake
- Round Glass Sustain - Dog-faced water snake
A Recent Study on Inflation in India
Why in News?
A recent report of SBI shows that the migration of labour from low-income states to high income states in search of employment opportunities is resulting in higher inflation in high income States in the South such as Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- State-wise analysis – High-inflation states - Among all 35 states/UTs during the period FY13 and FY25 Tamil Nadu inflation is higher than all India inflation for 9 years out of the last 13 years.
- Among the States, Kerala clocked the highest inflation rate of 7.3% in Feb, followed by Chhattisgarh 4.9%.
- Low-inflation states- Gujarat and Punjab has lower inflation than all India inflation for 9 years from the last 13 years.
- Northeast and Western regions have had lowest inflation against higher inflationary trends displayed by Southern and Eastern region.
- The region wise analysis of retail prices shows that southern states display a higher trend in prices for items like vegetables, cereals and most of the pulses.
- Primary trends suggest higher taxes levied on petrol/diesel, liquor, as also registration charges for automobiles and flats by the Southern states could be the driver of higher inflations.
- Going by the share of sales tax collection by states, Southern states hold the highest share, followed by Northern region.
- India’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation moderated to 7-month low in Feb’25 due to easing in food and vegetable prices, inflation in bigger states continued to outstrip the all-India inflation rate of the same month.
- Higher Rural inflation - There are 9 States among major states, where inflation in rural areas is higher than the all-India rural inflation. Similarly, there are 8 States where urban inflation is higher than all India urban inflation.
- Reason- Higher food prices and the rural basket of food items weight is higher than the urban weights.
- Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) - High income states have an average food inflation CAGR% of 5.26%, above national level CAGR% of 5.18 from FY14.
- Middle income group have an average CAGR% of 5.03% - and lower-income group’s average CAGR is at 4.95% during the same period.
- This shows the purchasing power of higher income groups has higher inflation.
Reference
The Hindu - SBI study on Inflation
SC’s Recent Question on Food Security
Why is in News?
The Supreme Court recently said states showed a high per capita growth when asked to highlight the development index but claimed 75% of their population was below poverty line when it came to subsidies.
The Indian government uses Below Poverty Line (BPL) to identify and target assistance to those with incomes below a specific threshold, considered to be living in poverty.
- Questions of Supreme Court - The SC asked about the contradicting behavior of states claiming high per capita income while having a significant population below the poverty line.
- The apex court asked whether the subsidized ration system, meant to provide food security to the deserving poor, was merely a ploy by governments to garner popularity.
- The court said corruption and mismanagement of the Public Distribution System must not be a ground to discourage its implementation.
- The court was hearing petitions seeking ration cards for migrant workers to ensure food security.
- Legal provisions - The court said the poor have a right to access at least 2 square meals a day in terms of their fundamental right to life under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Central government’s clarification - Union government was duty-bound under the National Food Security Act to provide food grains.
- She said the coverage under the Act was 81.35%. There was additional coverage for 11 crore people under the Anganwadi scheme, and further coverage for another 22-crore people.
- Challenges - The Supreme Court, in an earlier hearing, had taken strong exception to the delays in the implementation of its April 2023 order to provide ration cards to about 8 crore migrant workers registered on the e-Shram portal but not covered under the National Food Security Act.
- The court was then informed that the portal had 28.6 crore registrants. Of this, 20.63 crore were registered on ration card data.
- SC had argued that there could be more than 10 crore workers left outside the protective umbrella of the Food Safety Act as the statistics were based on the 2011 census.
- The population would have increased since then. The court had underscored the duty of a welfare state to include each and every migrant worker on the ration card roll expeditiously.
Reference
The Hindu - Supreme Court Question on High Per capita income
|
One Liners 22-03-2025
|
|
History, Art and Culture
|
|
Indo-U.S. Cultural Property Agreement
- Signed in – 2024.
- Aim – To prevent smuggling of Indian antiquities to USA.
- Features – It has provision for fostering cooperation and mutual understanding in the matters of technical assistance, illicit trade and pillage of cultural property.
- Agreement, being preventive in nature has no timelines or target numbers.
- Repatriation of antiquities – So far, 588 antiquities have been repatriated from USA, out of which 297 received in 2024.
|
|
Economy
|
|
Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme
- Launched in – 2021.
- Nodal Ministry – Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Objectives – To make India a global hub for high-tech production and attract multinational chip manufacturers.
- To generate 85,000 industry-ready manpower at B.Tech, M.Tech, and PhD levels specialized in semiconductor chip design.
- Activity – It provides the students a complete hands-on experience in chip design, fabrication, and testing.
- Participating Institutions – Academic institutions/R&D organizations, Start-ups and MSMEs.
|
|
Oeko Tex Certification
- It is a worldwide certification for textiles such as yarns, fabrics, buttons, linens, terry cloth, thread, and other accessory materials.
- It tests for harmful substances in raw, semi-finished and finished textile materials and products.
- In India – The North Eastern Handicrafts and Handlooms Development Corporation Ltd. (NEHHDC) under the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region, has obtained Oeko-Tex certification for eri silk from Germany.
- Significance – Certification ensures that the final product is safe for human use.
|
|
Eri silk
- It is one of the most durable and strong fibres.
- Properties – It provides cooling effect in the summer and warming effect in the winter.
- World’s only vegan silk – It distinguishes itself through an ethical production process where the silk moth is allowed to naturally emerge from its cocoon, leaving the silk intact.
- In India – It is mostly cultivated in tribal areas of Assam.
|
|
Agriculture
|
|
Radiation based Food Preservation
- Radiation processing of food – It involves controlled application of energy from ionizing radiations such as gamma rays, electrons and X-rays for food preservation.
- Working – It disrupts the biological processes that lead to decay.
- The interaction of radiation and radiolytic products of water with DNA impair reproducing capacity of microorganism and insects.
- In India – Presently, 37 Gamma Radiation Processing Plants are in private, cooperative, semi government and government sector.
- 21 plants out of 37 are capable of carrying out radiation processing of agricultural/ food products.
|
|
Environment
|
|
International Day of Forests 2025
- Celebrated on – March 21st every year.
- Declared by – United Nations in 2021.
- Aim – To celebrate and raise awareness about the vital role of all types of forests.
- To recognize the importance of trees and forests, and take action to protect them.
- 2025 theme – ‘Forests and Food’, which emphasizes the deep connection between forests and global food security.
|
|
Science
|
|
Technology Adoption Fund (TAF) scheme
- It is for promoting the Indian industry especially start-ups towards commercialization of early-stage space technologies.
- Launched by – Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe), Department of Space.
- Objectives – Upgradation of the existing space technologies and development of innovative products.
- Import substitution of components whose technologies have not matured in the Indian industry.
|
|
Criteria for Funding support to Space Technology Startups
- The startup should be under Indian management and control.
- The proposal of the startup shall have potential commercial value.
- The startup shall not source any funding from any other central & state government departments and/or ministries for the project forming the subject of their proposal(s).
|
|
National Cancer Grid (NCG)
- Established in – 2012.
- Established and managed by – Tata Memorial Centre (TMC), with the support of Department of Space, Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Objectives – To involve and implement uniform standard of cancer care across India.
- To offer state-of-the-art services for patients and to create human resources to tackle the rising need for cancer care.
- To run epidemiological intervention studies to prevent cancer.
- To direct cancer research in clinic and laboratory to offer cost effective solution to cancer in India.
- Network – There are 362-member organizations in the NCG.
|
|
Nuclear Energy Mission
|