Why in News?
A report conducted by Paani.Earth in collaboration with the International Centre for Clean Water on pollution levels in the Arkavati has revealed alarming levels of physicochemical pollutants.
The Central Pollution Control Board's Water Quality Criteria focus only on physicochemical properties of water rather than hazardous pollutants.

Why in News?
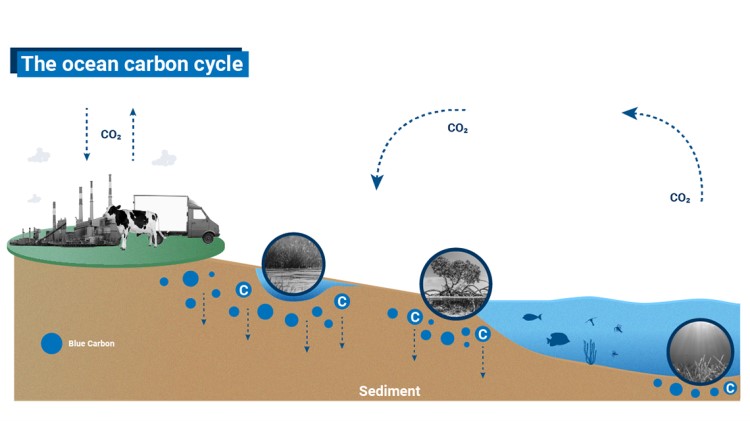
Current studies suggest that mangroves and coastal wetlands annually sequester carbon at a rate 10 times and store three to five times more carbon per equivalent area greater than tropical forests.
Mangroves alone have the capacity to store more than 1,000 tons of carbon per hectare.
Why in News?
Archaeological Survey of India have recently unearthed a colossal Buddha head, a massive palm, an ancient wall and inscribed Buddhist relics, all of which are estimated to date back 8th and 9th Century AD.
The links of Buddhism in Ratnagiri and Southeast Asia
The Indian Express | ASI excavation in Ratnagiri
Why in News?
The National Girl Child Day was celebrated every year on January 24.
|
Initiatives for Girl Child Development |
|
Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) |
|
|
UDAAN – A program to give wings to girl students |
|
|
Scheme for Adolescent Girls (SAG) |
|
|
National Scheme of Incentives to Girls for Secondary Education |
|
|
Scheme for Promotion of Menstrual Hygiene among Adolescent Girls in Rural India |
|
|
Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme |
|
|
Child Protection Services Scheme |
|
|
POSHAN Abhiyaan |
|
PIB| National Girl Child Day 2025
|
One Liners 24-01-2025 |
|
Geography |
|
Arkavathi River
|
|
Polity & Governance |
|
27th National Conference on Good Governance
Radar Equipment for the Measurement of Speed of Vehicles
Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLADS)
National Anubhav Awards Scheme
2nd Edition of Lok Samvardhan Parv
|
|
Security |
|
Hydrographic Survey Indian Navy completes hydrographic survey of 25,000 sq. nautical miles of Mauritius.
Aatmanirbharta
|
|
Miscellaneous |
|
Khelo India Winter Games (KIWG), 2025
Khelo India Scheme
|