BIMSTEC Charter comes into force after Nepal’s ratification.
BIMSTEC Charter came into force in the backdrop of stalled status of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) which last time met in Kathmandu during November 2014.
|
BIMSTEC |
|
References
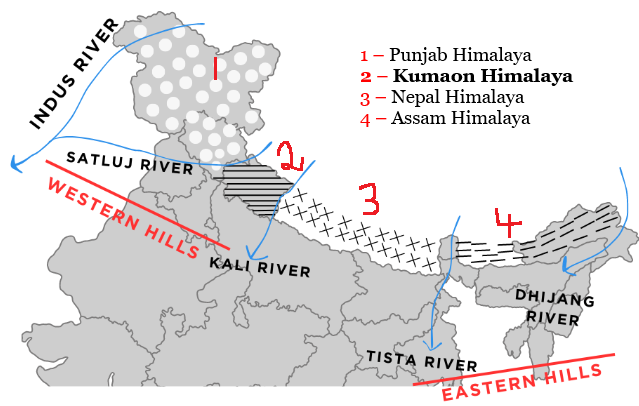
SC halts 90-acre project in Kumaon Himalayas on a plea challenging ‘single window’ clearances.
The 3 major geographical entities of Himalayas are the Himadri (greater Himalaya), Himachal (lesser Himalaya) and the Sivaliks (outer Himalaya).
Lake District of India, Nainital is India’s very own Lake District.Jim Corbett National Park in Nainital is the oldest national park in India, established in 1936 for the protection of the Royal Bengal Tiger.
Uttarakhand is home to 2 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, the Valley of Flowers and Nanda Devi National Park.
References
Indian government plans to expand irradiation process to boost shelf life of onion buffer stock.
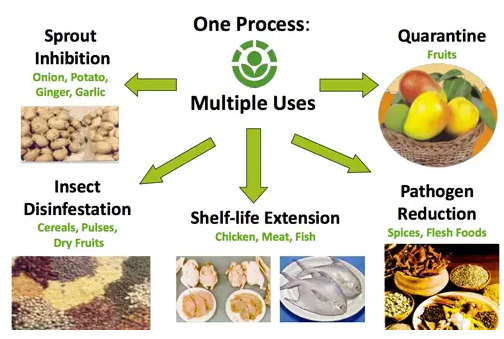
Quick Facts
References
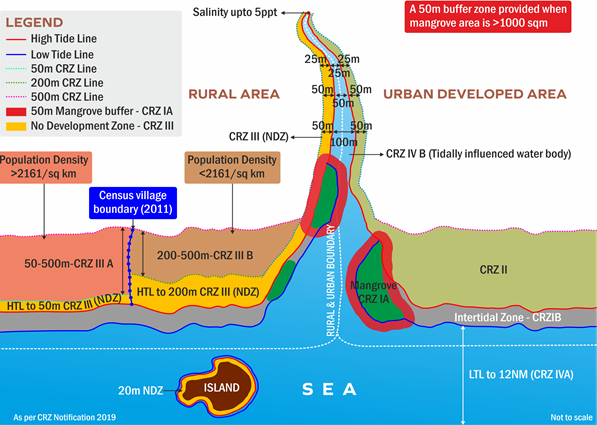
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) said that the Tamil Nadu State Coastal Zone Management Authority (TNSCZMA) nod is needed to set up facilities on Chennai city’s beaches.
High Tide Line (HTL) is the line on the land up to which the highest water line reaches during the Spring Tides. Low Tide Line (LTL) is the line on the land up to which the lowest water line reaches during the Spring Tides.
References
Government may look at addressing inverted duty structures in washing machines, air purifiers.

Input Tax Credit means the GST paid by a taxable person on any purchase of goods and/or services that are used or will be used for business.
References