Why in News?
GSLV-F15 NVS-02 mission is the 100th launch from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, scheduled for January 29.

Why in News?
A groundbreaking study reveals that Tamil Nadu's Iron Age began as early as 3,345 BCE, predating the Hittite Empire's iron usage by a millennium.
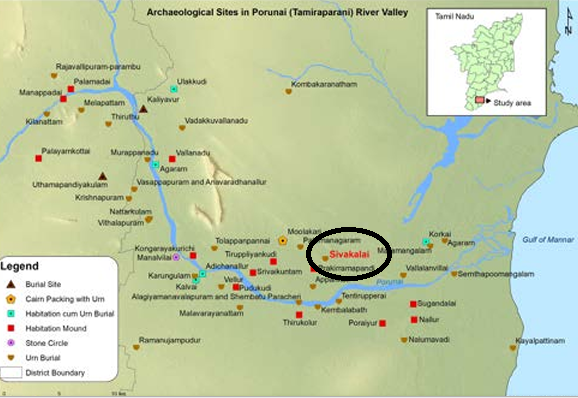

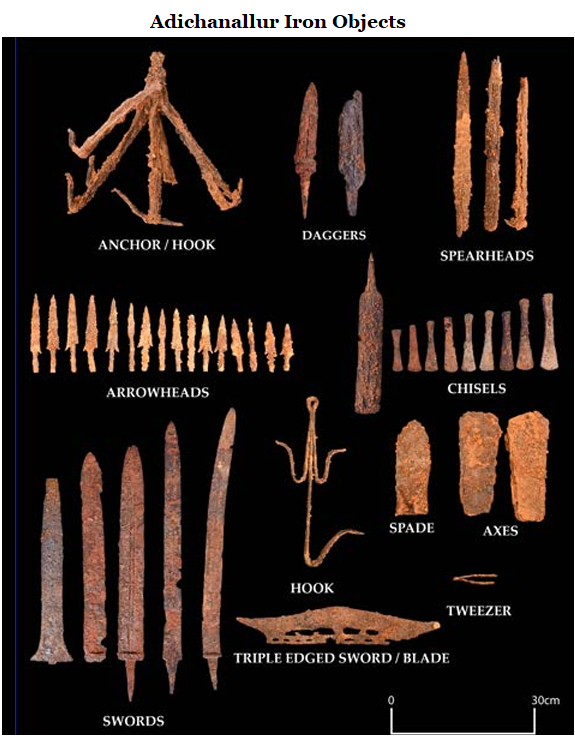
Why in news?
The Fiscal Health Index (FHI) was recently released by Niti aayog that provides a comprehensive assessment of the fiscal health of 18 major States.
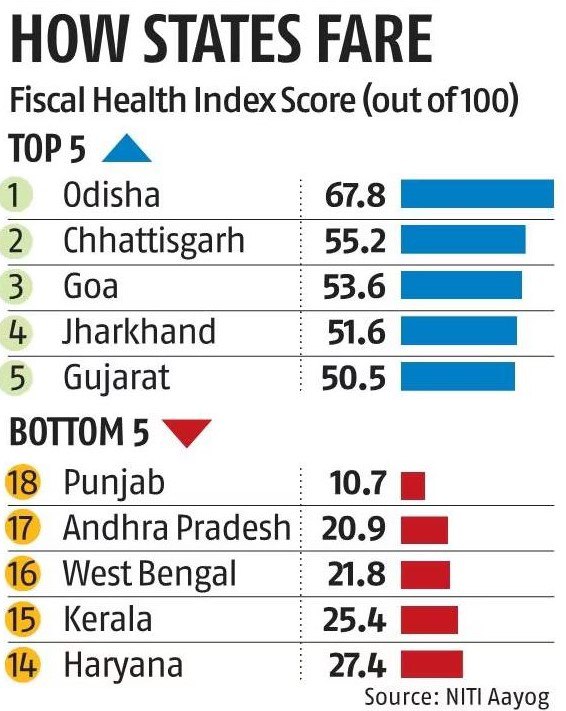
Why in News?
Recently, the data showed that in the past 5 fire seasons, over 11 lakh fires incidents reported in India.
India has reported a staggering 11,09,588 forest fires. Each year from November to June, forests across the country ignites, threatening ecosystems, wildlife and livelihoods.
The Hindu Business Line| India’s Forests Ablaze
|
One Liners 25-01-2025 |
|
History, Art and Culture |
|
76th Uttar Pradesh Foundation Day 2025
|
|
Geography |
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
|
Polity & Governance |
|
Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats and Tangible Incomes (MISHTI)
Digital Tree Aadhaar programme
PM Suryaghar Muft Bijli Yojana.
|
|
Security |
|
Pralay
SANJAY - The Battlefield Surveillance System (BSS)
|
|
Science |
|
International Solar Conference (ISC)
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KSO)
Artificial Sun Chinese scientists achieved a world record with artificial Sun.
|