Indus Water Treaty Suspension
Prelims – Current events of national and international importance.
Mains (GS II) – India and its neighbourhood - relations| Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in news?
India has declared the Indus Water Treaty (IWT) of 1960 with Pakistan "in abeyance" with immediate effect in response to terror strike in Pahalgam.
- Held in abeyance – India has temporarily suspended the enforcement of the treaty until Pakistan credibly and irrevocably abjures its support for cross-border terrorism.
- Scope of suspension – There is no explicit provision for treaty suspension in the original water treaty agreement.
- Article 62 of the Vienna Convention on Law of Treaties - Provide grounds for rejecting a treaty due to fundamental change of circumstances.
The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (VCLT) adopted on 1969 is an international agreement that regulates treaties among sovereign states.
Implications of Suspension
- India is no longer obligated to follow restrictions on reservoir flushing of the Kishanganga and other projects on western rivers (Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab) in Jammu and Kashmir.
Reservoir flushing is a technique used to remove accumulated sediment from a reservoir by releasing water at a high flow rate to wipe out the sediment.
- Reservoir filling can now be done anytime instead of only during August (peak monsoon).
- There are no operational restrictions on how reservoirs are to be filled and operated.
- There will be no restrictions on designing building structures like dams on western rivers.
- In the past almost every project has been objected to by Pakistan over the designs.
- India can stop sharing flood data on the rivers with Pakistan.
- India can take flood control measures to mitigate floods in the Valley.
|
Indus Water Treaty
|
- The Indus Water Treaty (IWT) is a water-distribution treaty between India and Pakistan.
- Negotiated by - The World Bank.
- Signed in - 1960.
- The treaty covers the Indus system of rivers which includes:
- The main Indus River
- Five left bank tributaries - Ravi, Beas, Sutlej, Jhelum, and Chenab
Water Allocation Under Treaty
- Eastern rivers (Sutlej, Beas, and Ravi)
- Allocated to India for unrestricted use
- Western rivers (Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab)
- Allocated largely to Pakistan.
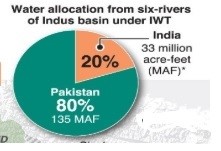
- India can use western rivers for domestic use, agriculture, and hydroelectric power.
|
Reference
The Hindu| Indus Water Treaty suspension
Related Article: Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)
Indigenous HPV Test Kits for Cervical Cancer Screening
Prelims – Current events of national and international importance.
Mains (GS III) – Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
Why in news?
Indigenous HPV (Human papillomavirus) test kits for cervical cancer screening were launched recently in New Delhi.
- Objective – To enable affordable, accessible, and ideally mass screening for cervical cancer.
- Developed by - Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) under Department of Biotechnology's (DBT) partnership programme Grand Challenges India (GCI).
The Grand Challenges initiative launched by Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation drives innovation (BMGF) to tackle critical health issues in developing nations.
In 2012, BMGF and DBT signed an MOU to launch Grand Challenges India, to foster health research and innovation.
- Developed in collaboration with International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).
The International Agency for Research on Cancer is an intergovernmental agency is a part of World Health Organization founded in 1965 to conduct and coordinate research on causes of cancer.
Key Features of the Test Kit
- Focused screening – The kits include only the 7-8 most common cancer-causing HPV types, making the screening more focused and relevant to the Indian population.
- RTPCR-based diagnostic – The kits use RTPCR (Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology, which is known for its high sensitivity and specificity in detecting viral genetic material.
- Efficient and cost-effective – The focused approach on the most relevant HPV types and the use of existing RTPCR infrastructure make these kits a cost-effective screening method.
- Point-of-care test –The testing is conducted close to the site of patient care where care or treatment is provided.
|
Cervical Cancer in India
|
- Cervical cancer is a cancer that develops in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus.
- Caused by - Human PapillomaVirus (HPV).
- 2nd most common cancer among Indian women.
- According to WHO data, 1 in every 5 women globally suffering from cervical cancer is from India,
- 25% of global cervical cancer deaths occurring in India often due to late diagnosis.
- WHO recommends transitioning to HPV testing with only two tests in a lifetime (at age 35 and 45) to reduce the burden of screening, making it easier for women to access screening programs.
- Target - Screen 70% of eligible women by 2030.
|
Reference
The Hindu| Indigenously developed HPV test kits
Emission Reduction Compliance Mechanism
Prelims | Current Events of National Importance
Mains (GS III) | Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Why in News?
The environment ministry has issued a draft notification proposing GHG emission intensity (GEI) reduction target under Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS), 2023.
- All traditionally high-emission industries in India such as aluminum, cement and pulp & paper are obligated to reduce their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to meet specific targets.
- Compliance mechanism under - Carbon Credit Trading Scheme, 2023.
- Notification - Industries have to reduce GEI within a specified time-period.
- If industries do not meet their GEI targets by reducing emissions for the respective compliance year, they will have to purchase carbon credit certificates from the Indian carbon market.
- In case an obligated entity fails to comply with the GEI target or fails to submit the carbon credit certificates equivalent to the shortfall for compliance, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) will impose ‘environmental compensation’ (penalty) for the shortfall.
- The penalty will be equal to twice of the average price at which the carbon credit certificate is traded during the trading cycle of that compliance year.
- The average price will be determined by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), which has finalized detailed procedures to fix GEI targets (in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent) for each of the high emission sectors from the 2023-24 baseline year.
- Environmental Compensation shall be paid within the 90 days from the day of such imposition.
- The targets are in sync with the country’s ‘net zero’ emission goal of 2070 and will contribute to meet its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDCs) climate action targets.
- It is expected that the move may also make these industries ready to face the European Union’s proposed Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which is to be implemented from next year.
- The CBAM is a tool to put a price through imposing border tax on carbon intensive goods, like iron & steel, aluminium and cement.
- India has, however, strongly opposed the EU’s move as it will put a tariff burden on such products of developing countries and impact their trade.
|
Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS), 2023
|
- It is a market-based mechanism for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- It aims to establish the Indian Carbon Market (ICM) and supports the country's climate goals.
- The scheme operates through a compliance mechanism and an offset mechanism, allowing entities to reduce emissions through various projects and trade carbon credits.
- Compliance Mechanism - Mandatory for specific sectors, such as power, cement, steel, and others, with specific emission intensity targets.
- Entities are required to meet these targets or purchase carbon credits from the ICM.
- Offset Mechanism - Incentivizes voluntary emission reduction projects from entities not under the compliance mechanism.
|
References
- MSN | Emission intensity reduction targets
- Energetica | Draft GEI target Rules
World Economic Outlook, 2025
Prelims– Economic and Social Development
Mains (GS - III) – Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Why in News?
India is poised to lead the global economy once again, with the World Economic Outlook projecting it to remain the fastest growing major economy over the next two years.
- Released by - International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Duration - Published twice a year.
- It provides projections for the near and medium term, covering advanced, emerging, and developing economies.
- The report supports the IMF’s economic surveillance and guides discussions on policy among member countries.
Recent Findings of the Report
- Global Findings - IMF projects global economic growth to be much lower, at 2.8% in 2025 and 3.0% in 2026.
- China’s GDP growth forecast for 2025 has been downgraded to 4.0%, down from 4.6% in the January 2025 edition of the World Economic Outlook.
- Similarly, the United States is expected to see a slowdown, with its growth revised downward by 90 basis points to 1.8%.
- Despite these revisions, India’s robust growth trajectory continues to set it apart on the global stage.
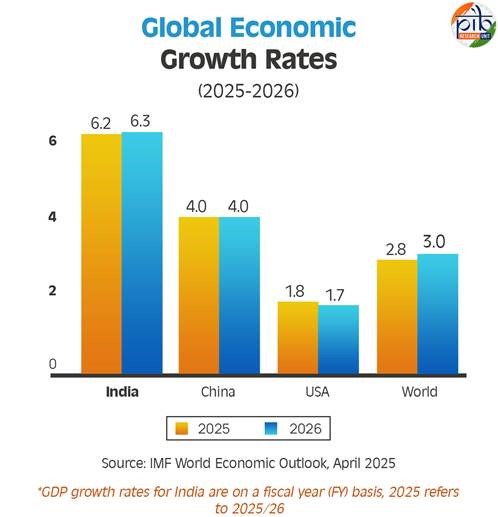
- Findings For India - The growth outlook is relatively more stable. The IMF projects steady expansion for the Indian economy, supported by firm private consumption, particularly in rural areas.
- In a global environment marked by uncertainty and subdued growth, India’s resilience stands out, reinforcing its role as a key driver of global economic activity.
- India’s economy is expected to grow by 6.2% in 2025 and 6.3% in 2026, maintaining a solid lead over global and regional peers.
- India is projected to remain the fastest-growing large economy for 2025 and 2026, reaffirming its dominance in the global economic landscape.
Reference
PIB | India: Fastest-Growing Major Economy
Recent findings on Earth’s Geological process
Prelims – Current events of National and International Importance
Mains (GS I) – Geography of the India & World | Important Geophysical phenomena
Why in News?
Scientists have recently discovered that a rare geological process is tearing the Indian Plate apart deep beneath the surface.
- Researchers revealed the India plate is delaminating, its dense lower layer peeling off and sinking into the Earth’s mantle.
- The process called delamination was detected beneath the Tibetan Plateau using seismic waves and helium gas analysis from natural springs.
- This shift could reshape earthquake patterns across the Himalayas and beyond.
- The findings reveal that parts of these plates especially their deeper sections can soften, break off, and sink back into the Earth over geological time.
- These findings have raised urgent scientific questions about the stability of one of Earth’s most active tectonic zones.
- Impact - The Himalayan region is already one of the most earthquake-prone areas in the world.
- With the Indian Plate tearing from below, new stress lines could be forming in the crust above.
- The tearing and sinking of the plate could create new stress points in the Earth's crust, triggering more frequent and potentially more powerful quakes.
- Particular attention is being paid to the Cona-Sangri Rift, a deep fracture in the Tibetan Plateau.
- Scientists believe it may be directly connected to this hidden tear. If confirmed, regions around this rift could face heightened earthquake threats in the coming decades.
- The implications go beyond India. The study suggests that delamination may not be unique to the Indian Plate.
- Researchers are now scanning other continental plates for signs of similar activity.
- Researchers continue to monitor seismic activity and helium levels across the region, using these tools to paint a clearer picture of the miles beneath the Earth's surface.
Reference
Economic Times | Hidden rift in Indian Plate
|
One Liners 25-02-2025
|
|
History, Art and Culture
|
|
Mehrgarh Farming Settlement
Recently, radiocarbon dating using Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) has adjusted the timeline of the farming settlement in Mehrgarh from 8000 BCE to 5200 BCE.
- Location – Mehrgarh, a Neolithic site, is situated at the entrance of the Bolan Pass in Balochistan, Pakistan.
- Early agricultural practices – The site reveals the presence of an early farming village with evidence of domesticated wheat, barley, and cattle.
- It is the earliest known location where cotton was utilized in the Old World.
- Excavations – Preserved mud brick structures, burial sites, and distinctive pottery known as Togau ware.
- Implications – The revised dating to 5200 BCE provides a more accurate chronological framework for understanding the development of early agriculture and settlement patterns in the region preceding the Harappan civilization.
|
|
Geography
|
|
Eruption at Poás Volcano
Recently, highly active Poás volcano, a significant tourist draw, has recently experienced an eruption.
- Location – Situated within the Poás Volcano National Park, Costa Rica.
- It is classified as a composite stratovolcano and reaches an elevation of 2,708 meters above sea level.
- Its irregular and complex structure covers a substantial basal area of approximately 400 square kilometers.
- Characteristics – It is characterized by its formation from several adjacent eruptive centers featuring large collapse craters.
- The volcano's principal crater is measuring about 1.5 kilometers in width and reaching a depth of 300 meters, ranking it among the largest active craters globally.
- Recent activity – Throughout 2024 and continuing into 2025, the crater lake has been drying up.
- Impacts – This process has triggered ash-producing eruptions and elevated gas levels, accompanied by small rock-ejecting explosions, indicating ongoing volcanic activity.
|
|
Internal security Issues
|
|
Pahalgam Terror Attack
Recently, horrific terrorist attack struck in Pahalgam, on April 22, 2025, resulting in the tragic deaths of more than 25 individuals, predominantly tourists.
- Located in – Baisaran Valley of Anantnag district, a well-known hill station in the Jammu and Kashmir Valley, approximately 90 km from Srinagar.
- Its remote, high-altitude location, accessible only by foot or horseback.
- Tourist site – The attack occurred in the scenic Baisaran Valley, a popular tourist destination renowned for its resemblance to European landscapes and often called "Mini Switzerland."
- Other tourist sites – Its attractions include the Amarnath Cave Temple, Aru Wildlife Sanctuary, Betaab Valley, and Tulian Lake, drawing numerous tourists annually.
|
|
Polity & Governance
|
|
Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (RPwD Act)
Recently, the Delhi High Court asked Swiggy and Zepto, to respond to a plea claiming their apps were not accessible to people with visual impairment.
- It was enacted to fulfill India's obligations under the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), which India ratified in 2007.
- Aim – To ensure the rights and dignity of people with disabilities.
- Replacement of – Persons with Disabilities Act, 1995.
- Feature – It mandates for adoption of accessibility features by the platforms such as e-commerce.
- Barriers to visually impaired persons – The platforms violated the dignity of persons with impairment by denying them equal access to essential services such as food delivery, grocery shopping, and restaurant reservations.
- The absence of accessible search features and interactive elements for the visually impaired created severe barriers.
|
|
Price Support Scheme (PSS)
Recently, the Government has approved the procurement of Tur, Urad and Masur under PSS equivalent to 100% of production for the procurement year 2024-25.
- Umbrella scheme – Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA).
- Objectives – To provide financial assistance to farmers when market prices for their crops fall below the Minimum Support Price (MSP).
- To protect farmers from losses due to price volatility and ensure they receive a fair return for their produce.
- Crops covered – Bajra, Jowar, Maize, Paddy, Cotton, Tur, Moong, Urad, Groundnut, Sesamum Wheat, Gram, Mustard, and Sugarcane etc.
- The procurement of oil seeds, pulses and cotton, through National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Ltd (NAFED), which is the Central nodal agency for the MSP.
|
|
Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS)
Recently, Surat’s ETS specifically designed to curb particulate air pollution, marking a significant step in environmental regulation.
- Launched in – 2019, it is the 1st unique scheme to focus on trading particulate pollution globally.
- Target – It initially targeted 342 high-emitting industries in Surat, predominantly within the textile sector, which commonly used solid fuels like coal and lignite, and liquid fuels such as diesel.
- Functions – A regulatory mechanism that uses economic incentives to lower air pollution.
- Establishes a limit (cap) on total allowable emissions, distributing tradable emission permits to industries.
- Enable companies to buy and sell pollution rights and industries with lower emissions can profit by selling surplus permits to those exceeding their limits.
- It also known as Cap-and-Trade System.
|
|
Economy
|
|
India's Manufacturing Push
Recently, Finance Minister outlined India's ambitious plan to elevate the manufacturing sector's contribution to GDP from 12% to 23% within the next 2 decades.
- Sunrise Industries – They are emerging sectors experiencing rapid expansion, characterized by high growth rates, numerous startups, and substantial investment.
- Characteristics – These industries are not static and mature over time.
- It potentially transitioning into maturity and eventually the sunset phase, as exemplified by the compact disc industry.
- These industries often exhibit significant innovation and their swift growth can pose a threat to established, declining "sunset" industries.
- Role – The targeted growth in India's manufacturing sector is expected to be significantly propelled by the dynamism and potential of these burgeoning sunrise industries.
- Examples – Alternative energy, social media, cloud computing, blockchain technology, information technology, and clean energy.
|
|
Environment
|
|
National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI)
The Supreme Court has recently directed the NEERI, to conduct a detailed assessment of the glass industries operating near the Taj Mahal in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, to evaluate their potential impact on the monument.
- Established in – 1958 in Nagpur, under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- It is a pioneering research institute in environmental science and engineering, funded by the Government of India and a constituent laboratory of Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR).
- The Central Public Health Engineering Research Institute (CPHERI), was renamed as National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI) in 1974.
- Mission – To undertake research and development in environmental management, pollution control, and sustainable development.
- Focus on – Water supply, sewage disposal, communicable diseases, and industrial pollution.
- Areas of Expertise – In climate/environment, health, lab and field testing, monitoring and evaluation, policy development, research, standards, technology, and fuel R&D.
|
|
Science
|
|
Quantum Gravity Gradiometers (QGGs)
Recently, NASA scientists are exploring the use of advanced cold atom-based QGGs deployed on satellites to precisely measure shifts in Earth's mass distribution, particularly those caused by climate change.
- It is a highly sensitive instrument that measures spatial variations in gravitational acceleration.
- Functions – To cool atoms near absolute zero in a vacuum, inducing wave-like behavior.
- Lasers manipulate these atoms, causing a phase shift directly proportional to the local gravitational force.
- Application – It is used in resource exploration to locate less dense hydrocarbon deposits, this technology is now being adapted for climate change monitoring.
- Measurement capability – This sophisticated setup allows for the detection of minuscule differences in acceleration, as small as 10−15m/s2 over a one-meter distance, enabling highly sensitive gravity measurements.
- Monitoring Earth's mass distribution – From low Earth orbit, QGGs can estimate the mass of significant geological formations like the Himalayas and monitor the movement of water, ice, and geological materials with unprecedented accuracy.
- The gravitational force across Earth's surface is not uniform; it varies based on the underlying mass distribution.
- Denser regions, such as mountain ranges, exhibit a stronger gravitational pull compared to less dense areas.
|
|
Miscellaneous
|
|
Special Category National Panchayat Awards, 2025
Recently, the Special Category National Panchayat Awards are conferred at the event of National Panchayati Raj Day (NPRD) on 24th April, 2025.
- It is the 1st time, that the Ministry of Panchayati Raj has institutionalised dedicated Special Category Awards.
- Objective – To incentivize and acknowledge exemplary efforts of Gram Panchayats in the key national priorities of Climate Action and Atmanirbharta (Self-Reliance) through augmentation of Own Sources Revenue (OSR).
- Climate Action Special Panchayat Award (CASPA) – To encourage Panchayats to act as climate-responsive local governments.
- Atma Nirbhar Panchayat Special Award (ANPSA) – To promote Atmanirbharta through augmentation of Own Source Revenue (OSR) by Panchayats.
- Panchayat Kshamta Nirman Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar (PKNSSP) – To recognize excellence in capacity building and training of Panchayati Raj representatives and functionaries.
- This award was instituted in 2023 and 1st awards were conferred in 2024.
|
