Western Hoolock Gibbon
As the world marks International Gibbon Day on October 24, the Western Hoolock gibbon, faces an unprecedented threat to its survival.
International Gibbon Day aims to raise awareness about gibbons and the challenges they face, as well as to promote efforts to protect these primates.
- Western Hoolock Gibbon is one of the 20 gibbon species in the world and India’s only ape species.
- Scientific Name - Hoolock hoolock.
- Family - Hylobatidae.
- It is also known as the white-browed gibbon.
- Currently there are less than 3,000 gibbons in India.
- Size - 1.5 feet tall and weighing 6 to 8 kilograms.
- Habitat - These primates are built for an arboreal life in forests from moist deciduous to evergreen, sub-tropical to lowland.
- Their hallmark brachiation, a special form of arboreal locomotion, enables them to swing up to 6 metres in a single leap, reaching speeds of over 50 km/h as they move effortlessly between trees.
- It can jump between 10 to 12 metres.
- Distribution - They are usually seen in the forests of Nagaland, Meghalaya, Manipur, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram and Assam.
- Appearance – It is tailless like other apes. Males have jet-black coats, while females are a rich brown.
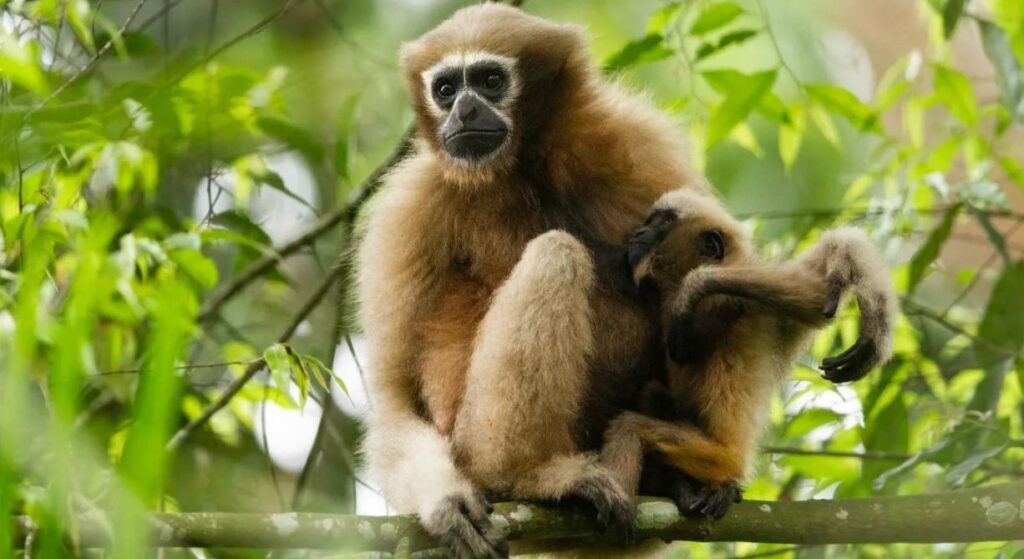

- Mating - Gibbons do not mate within family lines, and once paired, they formed lasting monogamous bonds.
- Calls - They are known for their distinct 'hook-o, hook-o, hook-o' calls, which can be heard from up to a kilometre away.
- Males and females often sing in unison, a series of duet calls that helps the pair to mark their territory.
- Diet - They are omnivorous, consuming over 100 species of plants and some invertebrates and birds’ eggs.
- Conservation status
- It is Asia’s most endangered primates.
- IUCN – Endangered.
- CITES - Appendix I.
- Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 - Schedule 1.
- Threats - Hunting for food and Medicine and Habitat loss, existential risk from a proposed oil exploration project near the Hollangapar Gibbon Sanctuary.
The western hoolock gibbon's population has declined by almost 90% in the last 30 years.
|
Hollangapar Gibbon Sanctuary
|
- It is the last remaining home of Hoolock Gibbon in Assam.
- It is formerly known as the Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary or Hollongapar Reserve Forest.
- The sanctuary was officially constituted and renamed in 1997.
- Bhogdoi River, a tributary of the Brahmaputra, flows along the sanctuary's border.
- It causes a waterlogged area characterized by plants that can thrive in partially submerged conditions, known as semi-hydrophytic plants.
- Flora - The upper canopy of the forest is dominated by the Hollong tree, while the Nahar dominates the middle canopy. The lower canopy consists of evergreen shrubs and herbs.
- Fauna - The sanctuary is home to the Bengal slow loris (Northeastern India’s only nocturnal primate), 219 bird species, over 200 butterfly species and rare reptiles.
- Indian elephants, tigers, leopards, jungle cats, wild boar, three types of civet, four types of squirrel, and several other types of mammal.
- Other primates include the stump-tailed macaque, northern pig-tailed macaque, eastern Assamese macaque, rhesus macaque, and capped langur.
|
Reference
- Times of India | Hollongapar Gibbon
- Kaziranga National Park | Hoollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary
Chief Justice of India
President Droupadi Murmu recently appointed Justice Sanjiv Khanna as the 51st Chief Justice of India.
- The Chief Justice of India (CJI) is the head of the judiciary and the Supreme Court of India, the custodian of the Constitution.
- The CJI is responsible for upholding the Constitution, ensuring justice for all citizens, and allocating cases.
- The CJI is also known as primus inter pares, which means "first amongst equals".
- Qualification - Apart from being an Indian citizen, the person must
- Have been for at least five years a Judge of a High Court or of two or more such Courts in succession or
- Have been for at least ten years an advocate of a High Court or of two or more such Courts in succession, or
- Be, in the opinion of the President, a distinguished jurist.
- Appointment – According to Article 124 of the Constitution of India, the President is pleased to appoint the Chief Justice of India usually from the senior-most judges in the Supreme Court.
- System - The system followed for recommending and appointing the Chief Justice of India is called the "Collegium System".
- The outgoing Chief Justice of India, in consultation with the 4 most senior judges of the Supreme Court, recommends the next Chief Justice to the President of India, who then appoints them.
- Essentially, the judiciary itself selects the next Chief Justice with the government having limited power to object to the recommendation.
- Term - They can hold office up to the age of 65 years or are removed through impeachment.
- Responsibilities
- Case allocation - The CJI allocates cases to specific benches.
- Constitutional bench appointments - The CJI appoints benches that deal with important legal matters.
- Administrative head - The CJI is the administrative head of the court.
According to Article 128, a retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called upon by the Chief Justice of India, with the prior permission of the President of India, to sit and act as a judge of the Supreme Court.
Reference
Indian Express | Chief Justice of India
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea, planet’s largest lake has been shrinking since the mid-1990s, but the rate it's disappearing has sped up since 2005.
- The Caspian Sea is the planet’s largest inland sea located between Europe and Asia.
- It is classified as a lake, despite being referred to as a "sea."
- Topography - It lies to the east of the Caucasus Mountains and to the west of the vast steppe of Central Asia.
- Coastline - Its looping coastline stretches more than 4,000 miles.
- Bordered by - 5 countries- Kazakhstan, Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia and Turkmenistan.
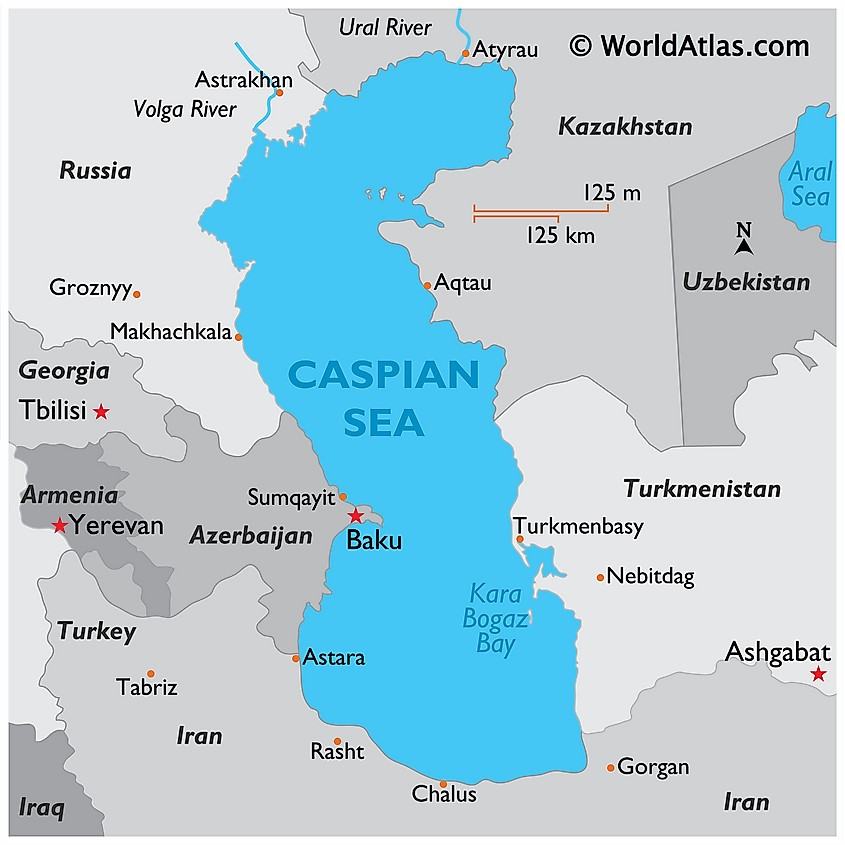
- Rivers - The Caspian is fed by 130 rivers, although around 80% of the water comes from the Volga, Europe’s longest river, which winds through central and southern Russia.
- The Caspian Sea is endorheic, meaning it has no natural outlets.
- Significance - Bordered countries rely on it for fishing, farming, tourism and drinking water, as well as its coveted oil and gas reserves.
- The Caspian also helps regulate this arid region’s climate, providing rainfall and moisture to Central Asia.
- Important Species - It is home to Caspian seals, an endangered marine mammal and critically endangered Beluga sturgeon.
- Threats - Damming, over-extraction, pollution and, increasingly, the human-caused climate crisis are driving its decline.
Reference
CNN | Caspian Sea
Scurvy
A disease once common among sailors and maritime communities, scurvy cases are now being reported in 2024 from Western Australia and Canada.
- It is a non-contagious severe vitamin C deficiency.
- Unlike most animals, humans cannot produce vitamin C naturally. Humans on the fruits and vegetables to provide this nutrient.
- Causes - Prolonged lack of vitamin C in the diet.
- Early symptoms - Weakness, fatigue, and sore limbs.
- As the disease progresses, symptoms can include:
- Gum disease
- Poor wound healing
- Skin hemorrhages
- Corkscrew hairs
- Personality changes
- Bleeding from the skin
- Treatment - The disease requires immediate treatment, as without it, scurvy can lead to serious complications and may even become life-threatening.
- Mild scurvy cases are often managed simply by increasing vitamin C intake through fresh fruits and vegetables. In some instances, taking vitamin C supplements is also recommended until symptoms improve.
- Prevalence - Scurvy was once widespread, particularly among 18th-century sailors who spent long periods at sea without access to fresh food.
- Significance of Vitamin C in Humans - Vitamin C plays a huge role in maintaining collagen, a protein important for tissues like skin.
- Vitamin C is also essential for healthy blood vessels, teeth, and gums, and it aids in iron absorption, necessary for red blood cell production.
- It also supports wound healing, including burns and cuts, by promoting tissue repair and immune response.
- Vitamin C is an antioxidant, meaning it protects your cells against damage from free radicals.
Reference
First Post | What is scurvy?
Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR)
The ICCR recently held a conference of Buddhist monks and scholars in Colombo on bequeathing Pali the status of a classical language by the Indian government.
- It is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of External Affairs.
- Aim - It is responsible to promote cultural exchanges with other countries and people.
- Founded in - 1950.
- Head Quarters - New Delhi.
- Objectives
- To actively participate in the formulation and implementation of policies and programs pertaining to India’s external cultural relations.
- To foster and strengthen cultural relations and mutual understanding between India and other countries.
- To promote cultural exchanges with other countries and people, and to develop relations with nations.
- Programs - ICCR administers various scholarship programs annually and awards about 3000+ scholarships under 21 different schemes to foreign students from about 180 countries.
- Amongst these 21 schemes, 6 are funded by ICCR from its grant and others are administered on behalf of MEA and Ministry of Ayush.
- The courses offered for studies are for Under-graduation, Post-graduation and Ph.D. levels.
- Each academic year, ICCR has about 6000+ of its foreign scholars who are studying at various Central/State Universities, Institutes, NITs, and Agricultural Institutions etc.
- The ICCR administers various programmes under which it hosts eminent personalities from abroad for a certain period.
- These programmes promote India's cultural relations with other countries through various instruments that involve people to people contact.
- ICCR developed the “Admissions to Alumni (A2A) Portal) to streamline the enrolment process.
References
- The Hindu | Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR)
- ICCR | About

