Virupaksha temple
A portion of the Virupaksha temple in Karnataka collapsed following torrential rains.
- Located in – Hampi, Karnataka.
- Establishment – Originally in 7th century, but it gained prominence in the 14th century during the Vijayanagara Empire.
- It was constructed in Lakkana Dandesha’s assistance who was a commander under King Deva Raya II.
The Vijayanagara Empire (1336 to 1646), founded by Harihara I of the Sangama dynasty, expanded from a strategic position on the banks of the Tungabhadra River.
- Dravidian temple architecture – 3 grand gopurams (towering gateways), the shikhara towering over the sanctum sanctorum, its intricate carvings and pillared halls.
- Gopuram – It depicts various deities, mythological scenes and animals as sculptures and carvings.
- Sanctum sanctorum – The Shiva lingam is the main deity.
Lord Virupaksha, also referred to as Pampapathi is the main deity in Virupaksha Temple. Virupaksha Temple complex also houses shrines of Bhuvaneshwari and Vidyaranya.
- Pavilions/ Saalu mantap – Supported by stone pillars
- Significance – It is the oldest and principle temple in Hampi.
- A vital centre for the religious and cultural activities of its time.
- Use of mathematical concepts – The temple is triangular in shape & the repeated patterns depict the concept of fractals.

- Destruction – Hampi was ruined by the Bahmani sultanates during Vijanagara-Bahmani rivalry.
- The pillars’ condition in the pavilion has deteriorated because of natural phenomena such as rain over a long period.
- Key challenges – Funding, logistics and human resources are lagging that slows the restoration work of the temple.
- Recognition – It belongs to the Group of Monuments at Hampi, declared as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The ASI is responsible for 57 out of the 95 monuments in Hampi that are nationally protected, while the rest are under the state government’s control.
|
Few important sites in Hampi ruins
|
- The Krishna temple complex,
- The Vitthala temple complex
- Virupaksha Temple
- Stone chariot Garuda shrine
- Pattabhirama temple complex
- Lotus Mahal complex
|
References
- The Indian Express| Damage of Virupaksha temple
- Karnataka| History of Virupaksha Temple
Naming of Cyclones
According to Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), Cyclone Remal will likely make landfall between West Bengal’s Sagar Island and Bangladesh’s Khepupara.
Cyclone Remal, the 1st pre-monsoon tropical cyclone in the Bay of Bengal in 2024, whose name means ‘sand’ in Arabic, was chosen Oman.
- PTC – Panel of Tropical Cyclones, established in 1972 by World Meteorological Organisation for naming tropical cyclones.
- 13 member countries – Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Myanmar, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Oman & Thailand were the 8 original members
- In 2018, Iran, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE and Yemen were included.
- Assigning name – In 2000, PTC agreed to assign names, each member to send its recommendations and finalised by PTC.
- Coverage – The tropical cyclones in Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea.
|
Guidelines in naming Cyclone – The proposed name
|
- Is neutral to (a) politics and political figures (b) religious believes, (c) cultures and (d) gender;
- Does not hurt the sentiments of any group of population over the globe or is not very rude and cruel in nature;
- Is short, easy to pronounce, and not offensive to any PTC member;
- Is at most 8 letters long;
- Is provided with its pronunciation and voice over; and
- Is not repeated (not before, not after).
|
The Panel of Tropical Cyclones (PTC) of started naming cyclones in the region in 2004.
- Name list – In 2020, a list of 169 cyclone names were released, comprises 13 suggestions each from the 13 countries.
- The countries are arranged in alphabetical order, all the names suggested by them are placed alongside in different columns with 1 name in each, totally 13 columns.
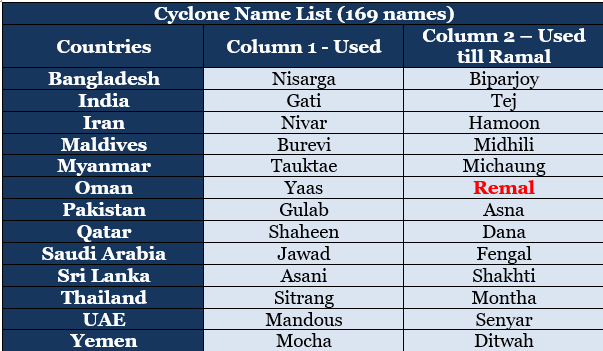
- Name allocation – The name in the 1st column is chosen
- For instance, the 1st cyclone was named Nisarga (by Bangladesh that hit Maharashtra, followed by Gati (India’s choice, hit Somalia), Nivar (Iran’s choice, hit Tamil Nadu).
- After all the names of 1st column are exhausted, names from the next column are chosen, again starting from Bangladesh (for instance, after Mocha, the next cyclone was named Biparjoy).
- New list – After this current list is exhausted, a new list will be submitted by PTC members.
- Significance of naming – It is easy to identify individual cyclones, create awareness of its development, rapidly disseminate warnings for disaster mitigation and management.
Reference
The Indian Express| Naming of Tropical Cyclones
Voting Methods in India
India’s electoral framework allows certain categories of voters to exercise their franchise even if they are unable to make it to the polling station on the day of voting.
- Rules – Under the Representation of the People Act, 1951 (RPA).
- Regular voting method – A voters must vote in person, at their designated polling station, on the date and hours fixed for the poll and using Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs).
- Alternate voting method – Certain categories of voters can exercise their franchise in different methods under exception.
|
Alternate Voting Methods
|
|
By post
|
Special voters, Service voters and Electors subjected to preventive detention (also through special messenger)
|
|
Facilitation Centre
|
Voters on election duty
|
|
Postal Voting Centre
|
Persons employed in essential services
|
|
Home/ hospital
|
Senior citizens, Persons with disability, Persons affected or suspected of having Covid-19
|
- Postal ballot – Section 60 of the RPA allows voters to vote remotely who cannot be physically present in polling stations.
- Polling takes place outside the polling station.
- It takes place without EVMs (EDC voters are an exception).
- Polling takes place before the designated poll date in the constituency.
Electronically Transmitted Postal Ballot System (ETPBS) for Service Voters features encrypted ballots sent electronically via a secure portal. While the ballot is transmitted electronically, voters return their completed ballots via post at no cost.
- Facilitation Centres – Located at training venues and designated offices which operate before the election and is videotaped.
- Postal Voting Centre (PVC) – Here, voters may come and cast a vote on any of the 3 fixed days from 9 AM to 5 PM.
- Home voting – It is for absentee voters where Booth Level Officers (BLOs) deliver Form 12D.
- If the elector opts for the Postal Ballot, then the BLO collects the form for home voting within 5 days of the election’s notification.
- Proxy voting – Service voters in the Armed and paramilitary forces can vote either by proxy or postal ballot, where the indelible ink is applied to proxy voter’s left middle finger.
- Assisted Voting – It is for who are unable to vote due to blindness or other disability.
- A voter can bring a companion over 18 years of age into the voting booth on their behalf and the indelible ink is applied to the companion’s right index finger.
- Voting in a different polling centre – It is applicable when a person on election duty is deployed in the same constituency where they are enrolled as a voter.
- Election Duty Certificate (EDC) can be issued by the Returning Officer to entitle the voter to vote at a polling station through EVM at a different polling centre.
- However, if they are on duty in another constituency, they are entitled only to a postal ballot.
Reference
The Indian Express| Voting Methods in India
Special Categories of Voters
Special exceptions are made for certain categories of voters to ensure that everyone gets to exercise their franchise.
- Eligibility – It is given by ‘The Conduct of Election Rules, 1961’.
- Special voters – Individuals like President, Vice President, Governors, Cabinet Ministers, other high-ranking dignitaries, etc. and their spouses as given under Section 20(4) of RPA.
- Service voters – Members and spouses residing with
- Indian armed forces
- Paramilitary forces
- An armed state police serving outside their state or
- A government employee stationed abroad.
- Voters on election duty – The public servants assigned official tasks on polling day
- All Commission’s observers
- Presiding officers, polling officers and agents
- Police personnel
- It also includes private individuals and non-government staff, such as videographers, drivers, helpline staff, etc., are also covered.
- Absentee voters – Created in 2019, under RPA, 1951.
- AVSC – Senior citizens aged 85+
- AVPD – Persons with disabilities having at least 40% disability
- AVCO – Covid-19 suspect or affected persons
- AVES – Persons employed in essential services (AVES).
- Classified Service Voters’ (CSVs) – They are voters who choose the proxy voting method.
- Service voters in the Armed and paramilitary forces can choose this method and they must appoint a local resident as their proxy.
Reference
The Indian Express| Special Categories of Voters
Treaty on Intellectual Property, Genetic Resources and Associated Traditional Knowledge
A new treaty was adopted at the Diplomatic Conference held under the aegis of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) at its headquarters in Geneva in 2024.
- Need – Under current laws inventions developed using genetic resources can be protected but genetic resources themselves cannot be patented.
- Parent body – World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
- Course of action - After adoption, the treaty was opened for signature and the treaty will enter force after 15 parties ratify it.
- However, signing the treaty at the end of a diplomatic conference does not commit a country to being bound by its provisions.
- Provision – Whenever there is a claimed invention on genetic resources, the applicants will have to disclose the country of origin or source of the genetic resources.
- imilarly, the applicant would also have to disclose the Indigenous Peoples or local community who provided the traditional knowledge, in case the patent is based on traditional knowledge.
- Significance – It is the 1st new WIPO Treaty in over a decade.
- It is the 1st one that deals with genetic resources & traditional knowledge held by Indigenous Peoples as well as local communities.
- It will not only safeguard and protect biodiversity but will increase transparency in the patent system and strengthen innovation.
India holds 7-8% of global biodiversity and a rich repertoire of knowledge based on these genetic resources.
- Challenges – It does not address the problem of the biopiracy of genetic resources & associated traditional knowledge using patents.
The Nagoya Protocol under the Convention on Biological Diversity does ensure that benefits earned through the use of traditional knowledge are shared with the communities that have protected the resource and the associated knowledge for centuries.
References
- Down To Earth| New WIPO Treaty on Genetic Resources
- PIB| WIPO Treaty, a win for Global South and India

