7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
PRAGATI Platform
GATI Portal
Bodoland Territorial Area
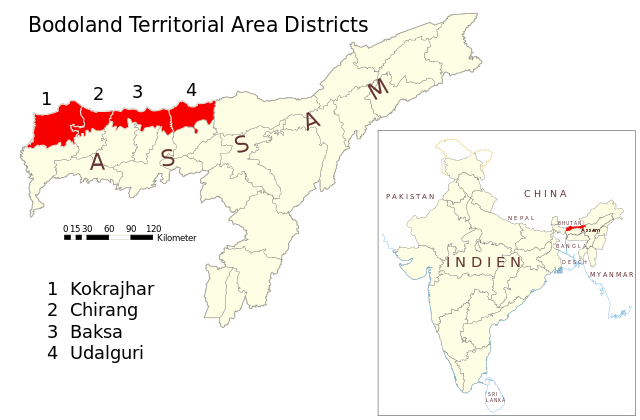
Bodo Accord
Locust Attack
Giant Tusked Elephant
G-77 Nations
Source: Indian Express, PIB, the Hindu