7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Recent analysis published by The Lancet reveals significant differences in disease burden and health outcomes between men and women globally.
|
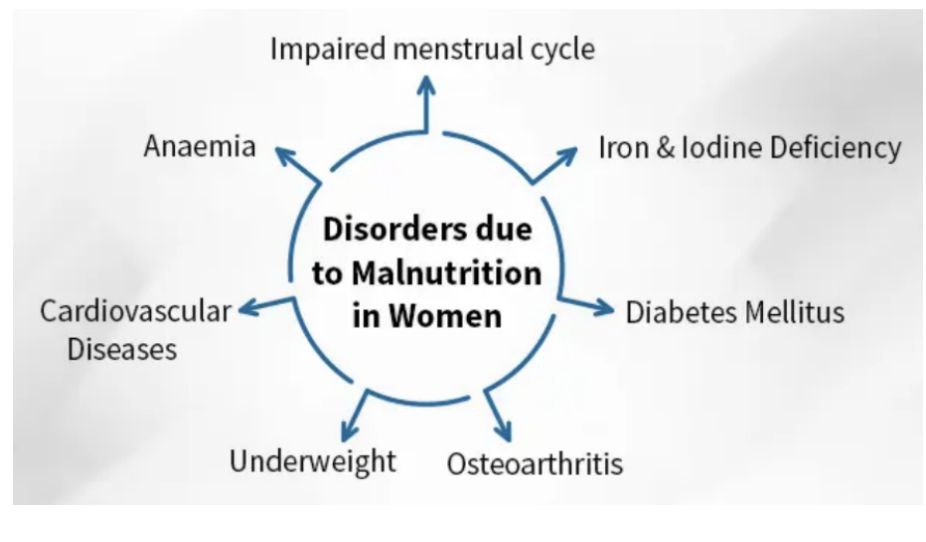
Status of women’s health in India |
|
|
Women |
More likely to suffer from lower back pain, depression, and headaches. |
|
Men |
Higher rates of premature death due to road accidents, cardiovascular diseases, and COVID-19. |
Causes of difference in disease burden